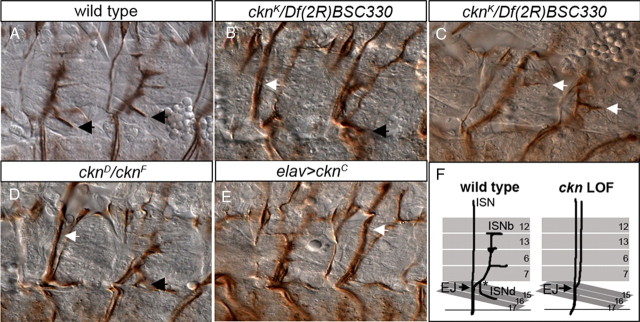
Figure 3.
ckn LOF alleles disrupt ISNb motor axon pathfinding. A–E, Two hemisegments of stage 16 embryos labeled with mAb 1D4 to mark motor axon projections. A, ISNb-projecting axons of wild-type embryos innervate four ventrolateral muscles and adopt a characteristic branched morphology. The black arrows indicate the ISNd branch (when present) in all panels. B, In cknK/Df(2R)BSC330 null embryos, ISNb axons extend in a distinct fascicle adjacent to the primary ISN branch (parallel bypass; white arrow) and do not enter their muscle field. C, cknK/Df(2R)BSC330 embryo in the plane of the VLM field. ISNb axons that bypassed the normal entry point into their muscle domain “reach back” to contact their targets (white arrows). D, In the cknD/cknK embryo, ISNb axons fail to innervate their muscle targets and extend with ISN axons in a common fascicle (fusion bypass; white arrow). E, In elavGAL4/UAS-cknC embryos, ISNb axons fail to separate from the ISN at the ventral choice point (arrow) and exhibit bypass. F, Schematic of wild-type and mutant ISNb/d nerve morphology. Exit junction (EJ) is the choice point where ISNb axons defasciculate from the ISN. The asterisk indicates the point of ISNb/d branch segregation. Anterior is to the left in all panels. Scale bar, 15 μm.