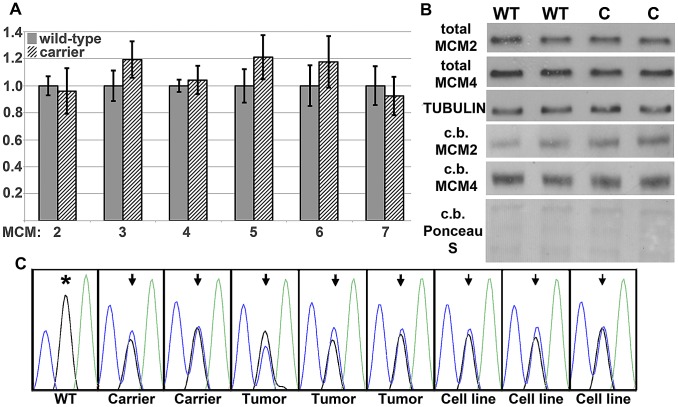
Figure 3. Mcm4D573H acts in a dominant manner to promote tumorigenesis.
WT = wild-type C = carrier. A) Mcm2–7 transcript levels are not decreased in Sdl carrier thymuses (striped bars) compared to wild-type thymuses (solid bars) as analyzed by qRT-PCR. Values for wild-type thymus are normalized to 1. N = 3 for wild-type, 6 for carrier. Error bars represent standard deviation. There is a trend toward increased expression of Mcm3 and Mcm5 in Sdl carrier thymuses compared to wild-type thymuses (p = 0.07 and 0.09, respectively); all other p values >.2. B) Western analysis on total thymus protein extract as well as purified chromatin bound (c.b.) fractions indicate that Sdl carrier thymuses harbor similar levels of MCM2 and 4 proteins as do wild-type thymuses. TUBULIN and Ponceau S membrane staining were utilized to demonstrate equal loading for whole cell lysates and chromatin bound fractions, respectively. C) Sanger sequencing traces of RT-PCR products demonstrate that both wild-type (G) and mutant (C) Mcm4 alleles are expressed in Sdl tumors and tumor-derived cell lines. RT-PCR products from 21-day-old wild-type and Sdl carrier thymuses are shown for reference. Arrow indicates dual G/C peak, asterisk indicates wild-type G peak.