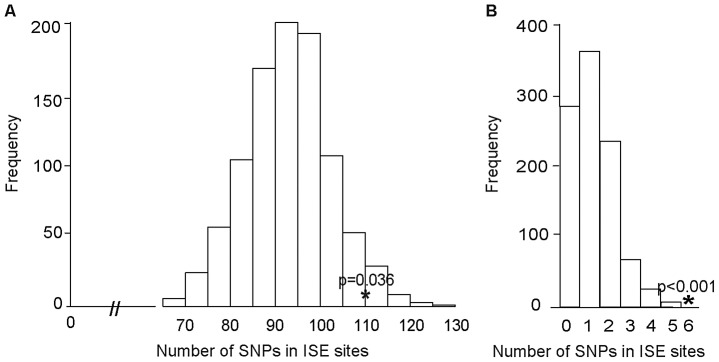
Figure 2. Enrichment of Exon Skipping–Associated ISE SNPs among Complex Human Trait-Associated SNPs.
(A) The distribution of the number of predicted exon-skipping ISE SNPs observed for each of the 1,000 random draws of the 3,353 SNPs from bins matched for minor allele frequency (MAF, CEU) and matched on the distance to the nearest exon (of the 3,353 human-trait associated SNPs downloaded from the NHGRI catalog) is shown in the bar graphs. The actual number of 111 predicted exon-skipping ISE SNPs observed in the 3,353 SNPs from the NHGRI catalog is shown as a solid asterisk. The distance to the nearest exon of intronic SNPs was calculated using Ensembl Gene predictions (ensGene.txt.gz) and the SNP annotation file (snp129.txt.gz) downloaded from the UCSC genome browser, http://hgdownload.cse.ucsc.edu/goldenPath/hg18/database/. For the distance to the skipped exon of ISE SNPs, we used exon skipping events from Ensembl Gene predictions. (B) The distribution of the number of predicted exon-skipping ISE SNPs observed for each of 1,000 draws of 49 SNPs from bins matched for MAF to the 49 SNPs associated with human tissue specific exons identified by Heinzen et al. [15] (bins include all SNPs in HapMap, CEU) is shown in the bar graphs, with the actual number of 6 predicted exon-skipping ISE SNPs observed in the 49 from Heinzen et al. shown as a asterisk.