Fig. 2.
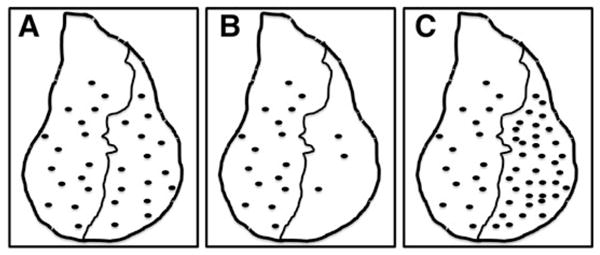
A schematic of different responses to radiation-induced cell cycle arrest. Following irradiation (500 rads of γ rays), the total number of pH3-positive cells is similar in the anterior and posterior compartments when only GFP was expressed in the posterior compartment (a), whereas fewer (b) and more (c) pH3-positive cells are found in the posterior compartments expressing particular UAS-cDNAs or UAS-RNAi trans-genes, respectively, indicating that such genes may control cell cycle arrest. Note that the anterior compartment of the discs serves as an internal control. It is possible to scale up such an assay for genome-wide genetic screening of molecules involved in the radiation-induced cell cycle arrest response.
