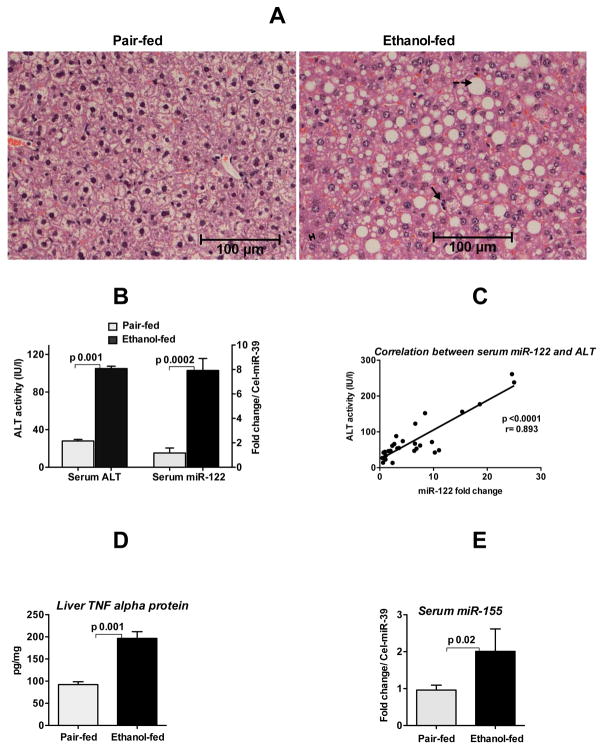
Fig. 1. Increased circulating miR-122 and miR-155 in alcoholic liver disease.
Eight-week old C57BL/6 female mice received Liber De-Carli diet either with 5% alcohol (alcohol-fed) or isocaloric diet (pair-fed) for 5weeks. A. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of liver sections fixed in formalin. Solid arrow indicates immune cells infiltrate, broken arrow indicates fat accumulation in hepatocytes and double arrow indicates mild necrosis of hepatocytes. B. ALT and miR-122 levels (TaqMan qRT-real time PCR) were measured in the serum as described in methods (n=6–8). C. Correlation between serum ALT and serum miR-122 was determined by Pearson method (n=30). D. The protein level of TNFα was measured from the whole cell lysate of liver homogenates by ELISA and normalized to protein concentration (n=6–8). E. MiR-155 expression was detected in the serum by TaqMan qRT-real time PCR (n=5). Synthetic C. elegans miR-39 was used to normalize Ct values. Fold change was calculated compared to pair-fed mice. Data represent mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed with Two-tailed t-test (B&D) or non-parametric Mann-Whitney test (E).