Figure 3. KATP channels mediate orexin neuron thermosensitivity.
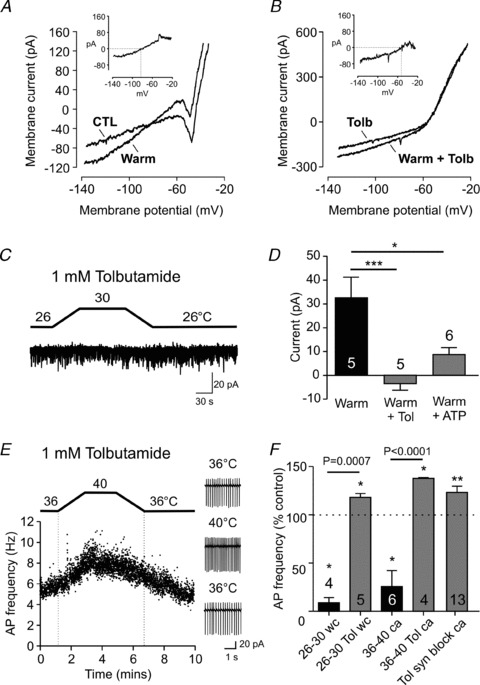
A, representative current responses to voltage ramps (−140 to −20 mV) recorded in the presence of TTX at baseline (CTL) and 4°C warmer conditions. Inset, a warming-induced current trace generated by subtracting CTL from Warm. B, the same experimental protocol as (A) except performed in the presence of tolbutamide, the KATP channel blocker. The reversal potential is more depolarized compared to the control condition shown in A. C, tolbutamide prevents the warming effect seen at the holding potential of −50 mV. D, summary graph showing that tolbutamide significantly blocks the warming-induced outward current (Warm + Tol). High ATP concentration (13 mm) in the intracellular solution also significantly attenuates the response to warming (Warm + ATP). *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.005, unpaired t test. E and F, tolbutamide unmasks an excitatory effect at physiological (36–40°C) and subphysiological (26–30°C) temperatures, which persists even when glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission is blocked by DNQX, d-AP5 and picrotoxin (syn block). wc: whole cell, ca: cell attached recording. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. respective baseline (paired t test). P values indicated above the horizontal bars correspond to statistical results between groups (unpaired t test). For D and F, numbers in bars represent the number of cells examined in each group.
