Figure 1.
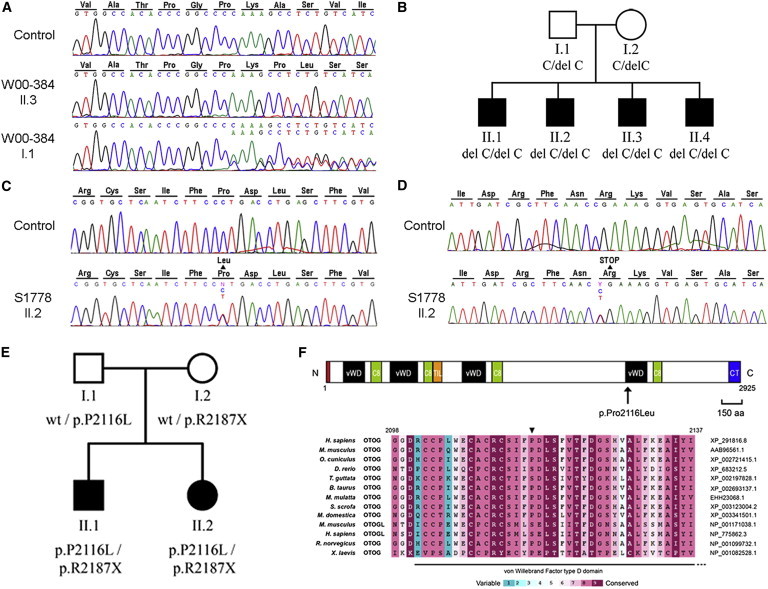
Mutation Analysis of OTOG
(A) Partial sequences are shown of OTOG exon 35 from an affected member and a parent of family W00-384 and a normal control. The amino acids are indicated above the sequence. The c.5508delC variant found is predicted to result in a frameshift and premature stop codon, p.Ala1838ProfsX31 (reference sequence XM_291816.8).
(B) Pedigree of family W00-384 and segregation of the c.5508delC variant.
(C) Partial sequences of OTOG exon 37 from a normal-hearing control and affected subject S1778 II.2, showing the c.6347C>T (p.Pro2116Leu) substitution.
(D) Partial sequences of OTOG exon 38 from a normal-hearing control and affected subject S1778 II.2, showing the c.6559C>T (p.Arg2187X) nonsense mutation.
(E) Pedigree of Spanish family S1778 and segregation analysis of the c.6347C>T and c.6559C>T mutations.
(F) Localization and conservation of the Pro-2116 residue. Above are shown domains of human otogelin. Red box, N-terminal signal peptide; vWD, von Willebrand factor type D domain; C8, domain containing eight conserved cysteine residues; TIL, trypsin inhibitor-like domain; CT, cystine knot-like domain. The localization of the p.Pro2116Leu missense mutation is indicated by an arrow. Below are shown alignment of diverse vertebrate otogelin (OTOG) and otogelin-like (OTOGL) amino acid sequences (accession numbers are shown on the right). ConSeq conservation scores are shown by the color scale. Residue Pro-2116 (arrowhead), located in the fourth von Willebrand factor type D domain, is highly conserved (score 8).
