Figure 2.
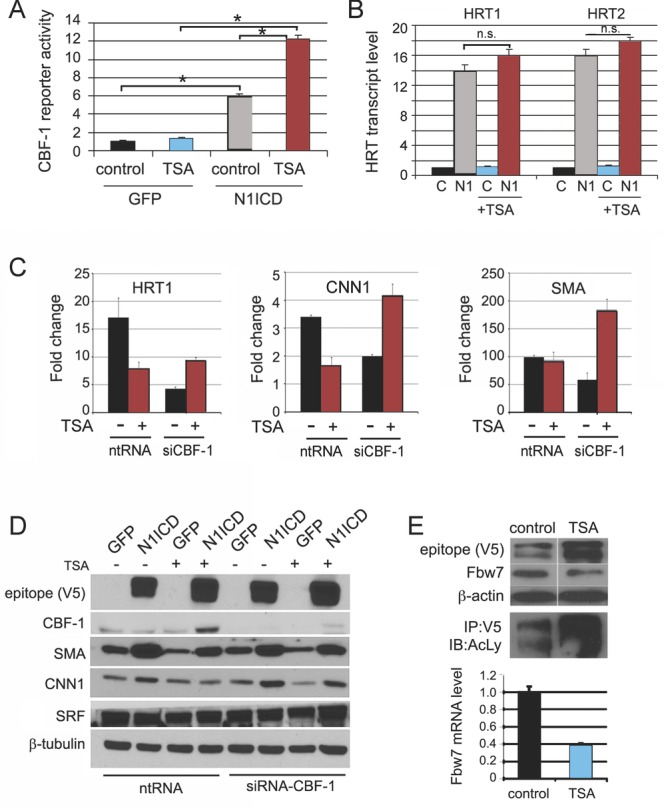
HDAC inhibition enhances Notch signaling and downregulates Fbw7. A, Primary human SMCs were transduced with green fluorescent protein (GFP) or Notch1ICD (N1ICD) and a CBF-1 luciferase reporter construct and were treated with TSA or control dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) for 48 h before analysis. Shown is normalized luciferase (mean±SEM). ANOVA / Tukey test was used for statistical analysis, and asterisks indicate P<0.05. Expression of N1ICD significantly increased reporter activity, even in the presence of TSA, and TSA further enhanced CBF-1 reporter activity in the presence of activated Notch signaling. B, GFP- or N1ICD (N1)–transduced SMCs were treated with TSA or control vehicle DMSO (C) for 48 h, and total RNA was collected for quantitative RT-PCR to measure HRT transcripts. Data were statistically analyzed by ANOVA / Tukey test, and HRT1 and HRT2 transcripts were significantly elevated with N1ICD or N1ICD+TSA compared to respective controls. There was no significant difference (n.s.) in N1ICD induction of HRT when TSA was included. C, CBF-1 was suppressed using specific siCBF-1 compared to nontargeting control (ntRNA), and quantitative RT-PCR was used to measure HRT1, calponin1 (CNN1), and SM actin (SMA) mRNA in the absence or presence of TSA. D, Protein lysates were collected from cells under the same conditions as in C and were used for immunoblot as indicated. E, N1ICD-transduced SMCs were treated with TSA or control vehicle DMSO for 48 h before analysis by immunoblot or quantitative RT-PCR to detect Fbw7 protein and transcript, respectively. Under the same conditions, 10% of total cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-V5 and immunoblotted with an antibody recognizing acetylated lysine (AcLy).
