Figure 5.
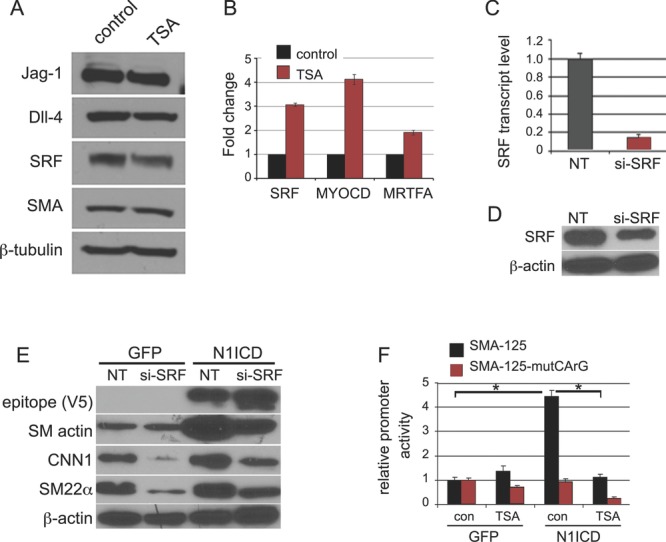
SRF is required for Notch-mediated SMC differentiation. A and B, Primary human SMCs were treated with TSA or vehicle control dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) for 48 h before Western blotting for Jag-1, Dll-4, SRF, and SMA protein levels (A) or quantitative RT-PCR analysis for SRF, myocardin (MYOCD), and MRTFA transcript levels (B). Data are presented as fold change as compared to SMCs treated with DMSO control. Human SMCs were transduced with a nontargeting siRNA (NT) or with siRNA targeted against SRF (si-SRF) for 4 days and were collected to examine the efficiency of knockdown by quantitative RT-PCR (C) and immunoblot (D). E, NT- or siSRF-transduced SMCs were infected with green fluorescent protein (GFP) or Notch1ICD (N1ICD) for 3 days and were collected for analysis of SMC markers. F, SMCs were transduced with GFP or N1ICD with the SM actin promoter reporter construct (SMA-125) or the construct with the mutant CArG box (SMA-125-mutCArG). Cells were treated with TSA or control vehicle DMSO (con) before analysis. Data are presented as fold change compared to SMCs with control DMSO treatment. Data are presented as mean±SD, and asterisks indicate P<0.05. SMA-125 activity was significantly increased with N1ICD compared to GFP, and this activity was significantly reduced with TSA.
