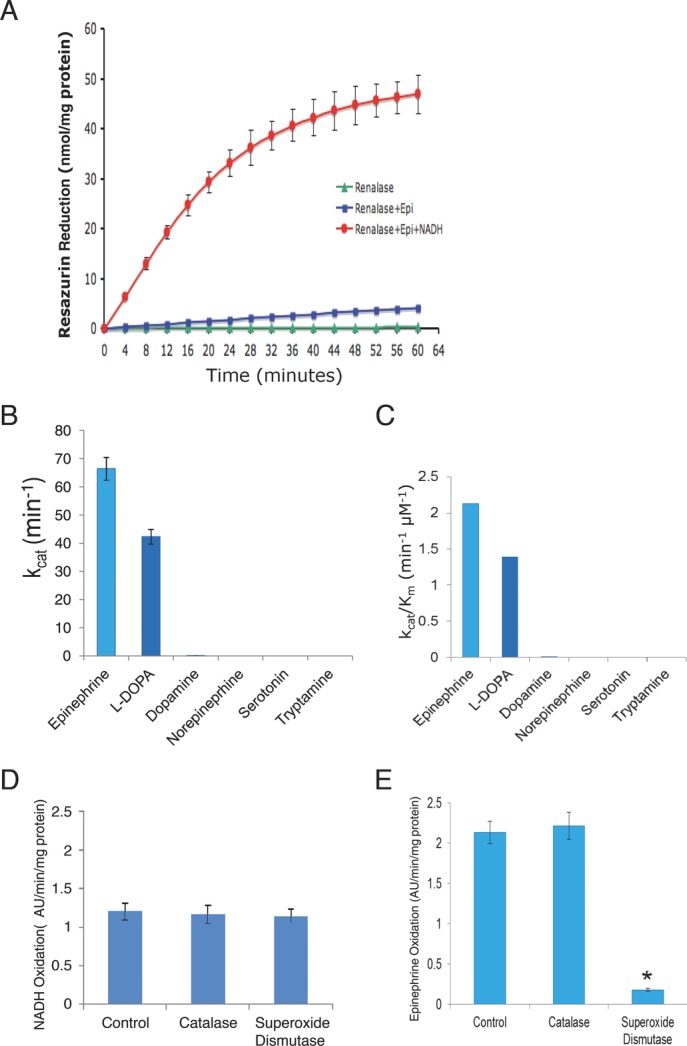
hRenalase1's physiological substrates: epinephrine and l‐DOPA. A, Effect of NADH on renalase's enzymatic activity. Epi indicates 200 μmol/L epinephrine; NADH, 250 μmol/L nicotimamide adenine dinucleotide. Values are mean±SEM; n=3. B, Catalytic rate for selected compounds. Data shown represent steady‐state rate of substrate oxidation by hRenalase1 in 25 mmol/L Tris, pH 7.5, 5 mmol/L NaCl, and 1.5 mmol/L NADH, at 37°C. Dopamine consumption was measured directly by HPLC. Values are mean±SEM; n=4. C, Catalytic efficiency of hRenalase1. n=4. D, NADH oxidation is unaffected by catalase and SOD. E, Dependence of epinephrine oxidation on superoxide anion. Control indicates hRenalase1 in 25 mmol/L Tris, pH 7.5, 5 mmol/L NaCl, and 1.5 mmol/L NADH, at 37°C; Catalase, 100 U catalase added to control reaction; SOD, 100 U SOD added; and AU, change in absorbance at 340 nm. n=5 for each group; Control compared to Superoxide with the Mann‐Whitney test. *P<0.05.
