Figure 6.
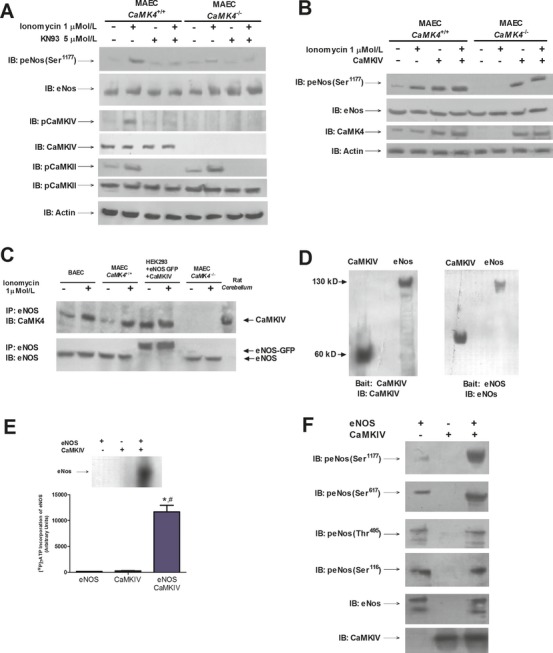
Interaction between CaMKIV and eNOS. eNOS phosphorylation (Ser1177) is enhanced by ionomycin, echoing the phosphorylation of CaMKIV, and is prevented by the CaMK inhibitor KN93 (A). Notably, eNOS activation was less evident in CaMK4−/− MAEC, where CaMK4 was not expressed (A). Transgenic restoration of CaMKIV expression in CaMK4−/− ECs corrected calcium-induced eNOS activation (B). The interaction between CaMKIV and eNOS was demonstrated by performing immunoprecipitation (IP) experiments in different cellular settings, both in basal conditions and after stimulation with ionomycin (C). Such interaction is shown in BAEC and CaMK4+/+ MAEC but not in CaMK4−/− MAEC. In a nonendothelial cell type, HEK293, we confirmed the interaction after reconstituting the system by using a plasmid encoding CaMKIV and a plasmid encoding eNOS linked to GFP (C; rat cerebellum was used as CaMKIV-positive control). The input protein levels are shown in Figure 8. Overlay assay with purified CaMKIV (left blot) or eNOS (right blot) as bait (D). CaMKIV induced eNOS [32P]-γATP incorporation (E). Purified CaMKIV induced eNOS phosphorylation on Ser1177 and Ser615 but not on Ser114 and Thr495 (F). *P<0.05 vs eNOS, *P<0.05 vs CaMKIV; representative images from triplicate experiments are shown. Densitometric analyses are reported in Figure 7. MAEC indicates murine aortic ECs; BAEC, bovine aortic ECs.
