Figure 4.
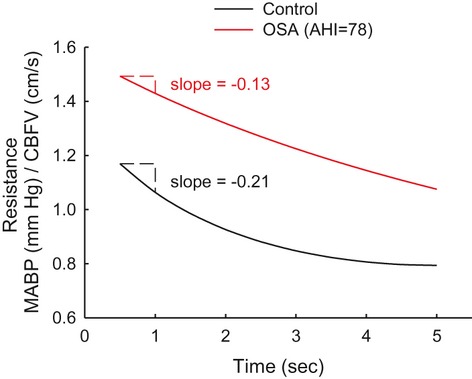
Resistances to blood flow through the middle cerebral artery in control subjects (n=26) and patients with OSA (n=78) after an orthostatic hypotension challenge, obtained by having individuals stand from a squatting position.105 The patients with OSA had a mean AHI of 78. The resistance was calculated by dividing mean arterial blood pressure (MABP) by blood flow velocity in the middle cerebral artery (CBFV). The increased resistance in the patients with OSA during orthostatic hypotension indicates that autoregulatory mechanisms responsible for dilating cerebral arteries were impaired relative to the control subjects. The response of the cerebral circulation to the hypotensive challenge was less dynamic in patients with OSA during the initial phase of the hypotensive challenge. That is, the rate of change in resistance in patients with OSA was only 62% of that in control subjects (100×[−0.13/−0.21]). Created with data from Urbano et al.105
