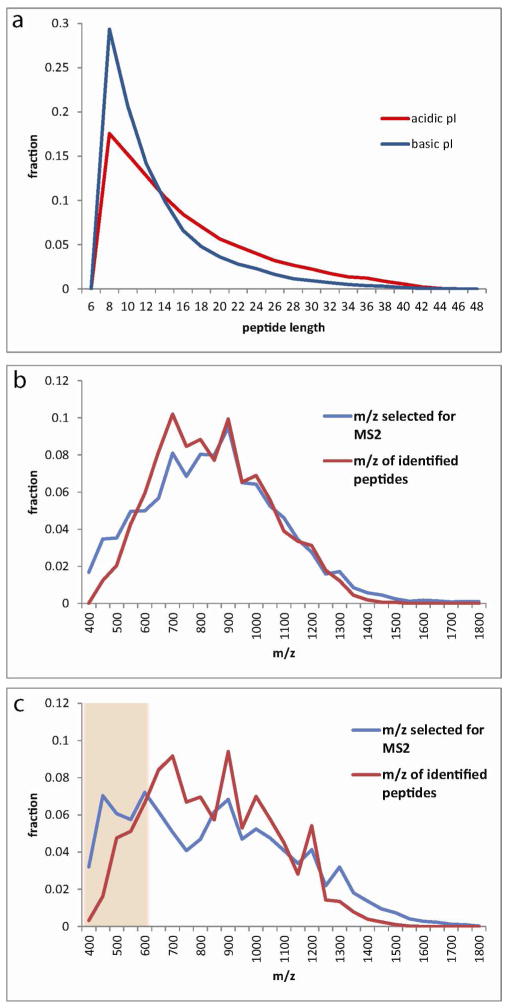
Figure 4.
Mechanism for the improved identification rate in ERLIC compared with RP. (a) An in silico tryptic digest of the yeast proteome shows that acidic peptides tend to be longer than basic peptides. (b) Comparison of the distribution of all m/z values selected for MS2 analysis in online ERLIC-MS and the m/z values of only those precursors resulting in identified peptides. The distributions match closely. (c) Comparison of the distribution of all m/z values selected for MS2 analysis in online RP-MS and the m/z values of only those precursors resulting in identified peptides. In RP, a relatively high proportion of precursors in the 400–600 Th range are being selected for MS2 analysis. These MS2 scans are unproductive, as the short peptides are unlikely to produce a PSM with sufficient confidence.