Fig. 1. MOG35-55 i.v. inhibited IL-17 and the development of EAE.
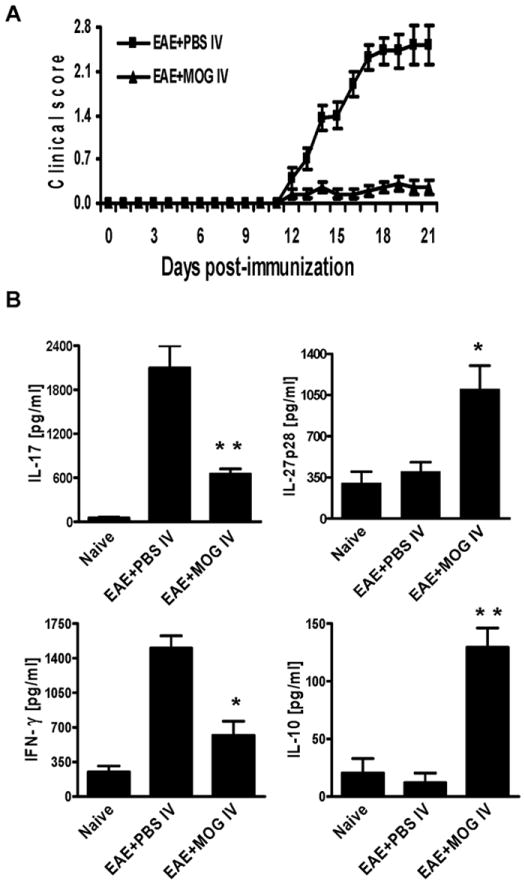
EAE was induced in B6 mice by immunization with MOG35-55/CFA and injection of pertussis toxin on days 0 and 2. At days 0, 3, and 6 p.i., mice were i.v. injected with 150 μg MOG35-55 peptide or the same volume of PBS to serve as EAE control mice. (A). Daily clinical scores of each mouse group (n = 10 each group; pooled from two independent experiments). (B) Cytokine expression in culture supernatants. 5 ×106 splenocytes in duplicate from mice in (A) were stimulated with 10 μg/ml MOG35-55 for 72 hrs. Cell-free supernatants were collected and analyzed for the expression of IL-17, IFN-γ, IL-27p28 and IL-10 by ELISA. Data were pooled from two independent experiments and presented as mean value/group ± s.e.m. (n =10 each group). * p<0.05; ** p<0.01 as comparison between EAE + PBS i.v. and EAE + MOG i.v. mice.
