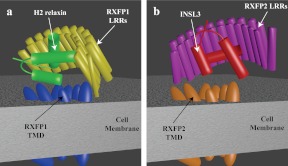
Fig. 6.
Schematic representation of how RXFP1 and RXFP2 may bind H2 relaxin and INSL3. A, H2 relaxin binds to RXFP1 with the relaxin B chain α-helix binding across the face of the LRR at an angle of 45°. This positions the A chain N-terminal α-helix across the extracellular loops of the TMD of RXFP1. Interactions between the LRR and the TMD of RXFP1 hold the receptor in the conformation needed to coordinate the sites and facilitate H2 relaxin binding. These interactions, however, hinder the binding mode of INSL3 to the ECD, which requires a 90° binding angle between the LRR β-strands and the B chain α-helix (B).