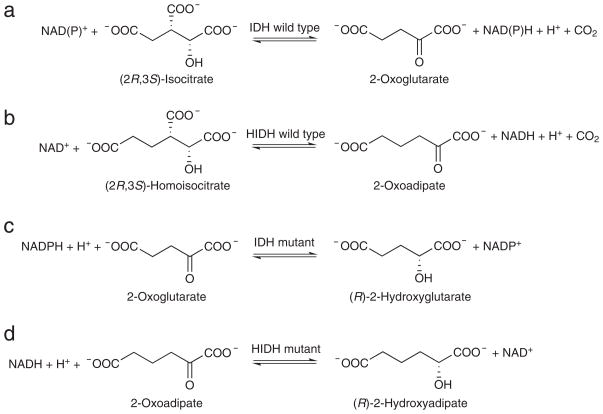
Figure 1. Strategy for enzyme mutagenesis.
(a) IDHs catalyze the NAD(P)+-linked reversible oxidative decarboxylation of (2R,3S)-isocitrate to form 2-oxoglutarate and CO2. (b) HIDHs catalyze the NAD+-linked reversible oxidative decarboxylation of (2R,3S)-homoisocitrate to form 2-oxoadipate and CO2. In the reverse direction, HIDHs catalyze the reductive carboxylation of 2-oxoadipate with CO2 to form (2R,3S)-homoisocitrate. (c) In human cancer, IDH mutants such as HsIDH1-R132H catalyze the non-carboxylating reduction of 2-oxoglutarate to (R)-2-hydroxyglutarate. (d) Analogous HIDH mutants could catalyze the non-carboxylating reduction of 2-oxoadipate to (R)-2-hydroxyadipate, i.e., (R)-2-hydroxyadipate dehydrogenases.