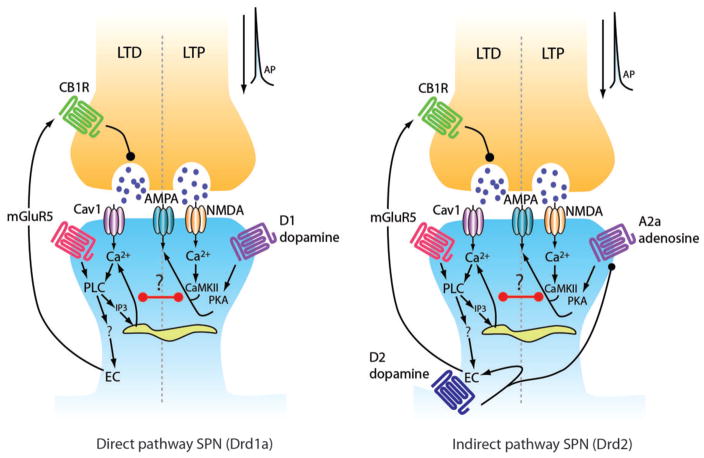
FIGURE 3.
Synaptic plasticity in direct and indirect SPNs. The presynaptic glutamatergic terminal is shown above (orange) and the postsynaptic spine shown below (blue). Black arrowheads depict positive regulation and black circles depict negative regulation. Purple circles in the synaptic cleft represent glutamate. Non-standard abbreviations: CB1R: cannabinoid receptor type 1; AMPAR: α-amino-3-hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionate (AMPA) receptor; N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA) receptor; Cav1C: Cav1 containing calcium channel (L-type); PLC: phospholipase C; PKA: protein kinase A; CaMKII: calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type II; IP3: inositol trisphosphate; D1R: D1 dopamine receptor; D2R: D2 dopamine receptor; EC: endocannabinoid; mGluR5: metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5; LTD: long-term depression; LTP: long-term potentiation. From Surmeier et al., 2009.