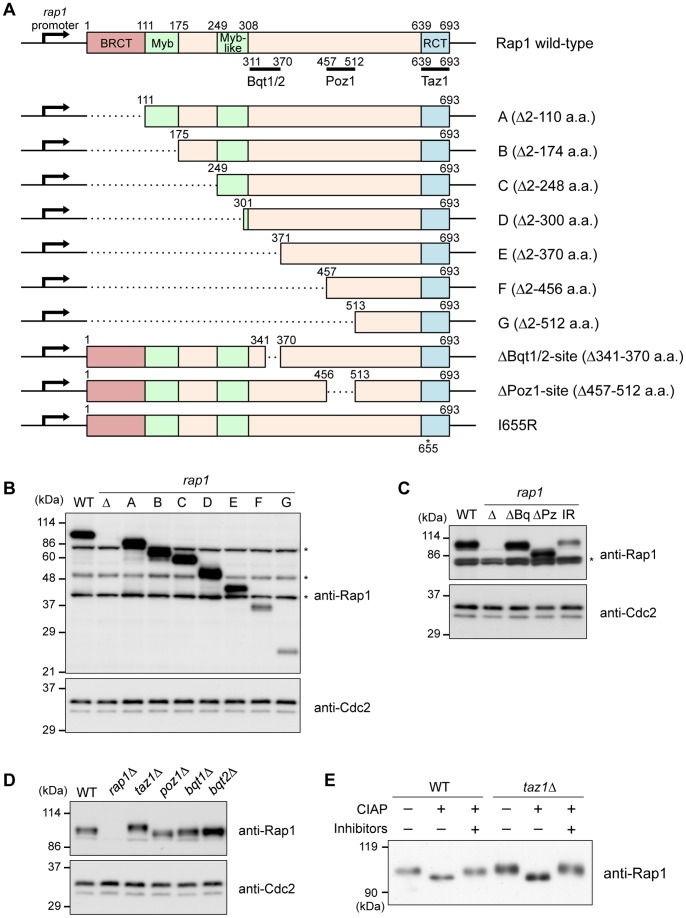
Figure 2. Expression of the Rap1 proteins in various mutants.
(A) Schematics of a series of rap1 deletions at the rap1 + locus. The binding sites for Bqt1/Bqt2, Poz1, and Taz1 are indicated by black bars below the Rap1 wild-type. In the rap1-I655R mutant, the Ile655 residue was mutated to Arg. (B) Expression of the Rap1 proteins. The whole cell extracts from asynchronous cells were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Rap1 antibodies. WT, wild-type; Δ, rap1Δ. Asterisks indicate non-specific bands. Cdc2: loading control. (C) Expression of the Rap1 proteins in each strain was analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Rap1. ΔBq, Bqt1/2-binding site deletion; ΔPz, Poz1-binding site deletion; IR, rap1-I655R. (D) Expression of the full-length Rap1 proteins in the various gene deletion mutants. The whole cell extracts of each strain were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Rap1. (E) Rap1 is highly phosphorylated in taz1Δ. Cells were grown to mid-log phase. Rap1 proteins were immunoprecipitated from the cell extracts using anti-Rap1 antibodies and treated with CIAP for 1 h at 32°C with or without phosphatase inhibitors. The samples were analyzed by immunoblotting using anti-Rap1.