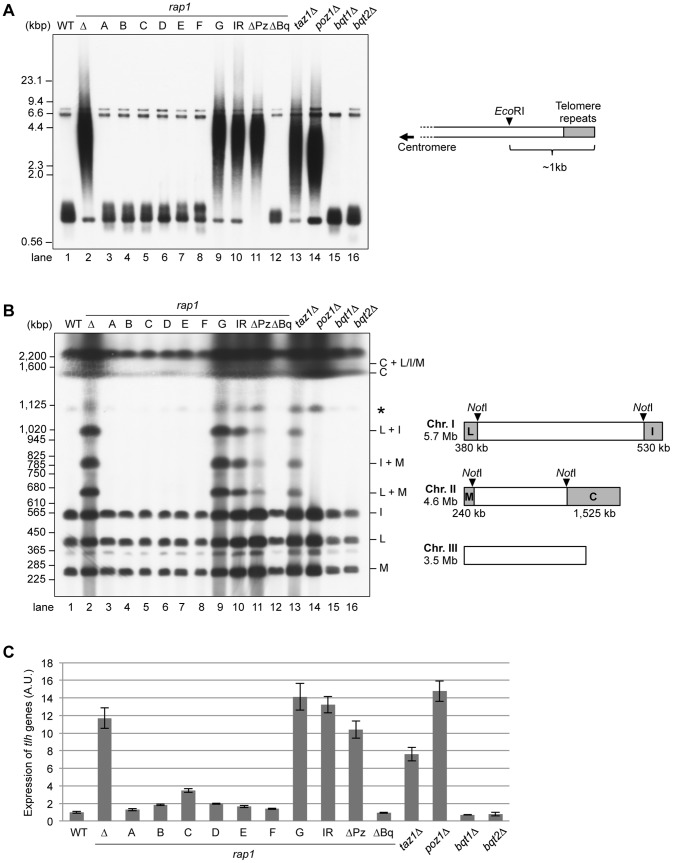
Figure 3. The Poz1- and Taz1-binding sites are critical for the maintenance of telomere structure.
(A) Southern blot analysis of the telomere DNA length. Genomic DNA was extracted from each strain grown in YES, digested by the restriction enzyme EcoRI, and separated on a TAE-1% agarose gel. The EcoRI digestion generates ∼1-kb fragments containing the telomere repeats from chromosomes I and II in the wild-type (right). A probe specific for the telomere repeats was used to detect the telomere ends. ΔBq, Bqt1/2-binding site deletion; ΔPz, Poz1-binding site deletion; IR, rap1-I655R. These data were reproduced using the other strains carrying the same rap1 alleles (Figure S1A). (B) Telomere end protection in G1-arrested cells. The strains used in (A) were grown in EMM, shifted into EMM–N (without nitrogen), and incubated at 28°C for 24 hours. Chromosomal DNA was prepared in agarose plugs and separated by PFGE after NotI digestion. The gel was transferred to a nylon membrane and hybridized with a probe specific for telomere repeats. The letters on the right side of the southern blot indicate the identities of the NotI-digested chromosomal DNA fragments. An asterisk indicates the bands, which probably correspond to the incompletely digested DNA fragment containing the “L” fragment of the chromosome I. (C) Telomere gene silencing. RNA expression level of sub-telomeric tlh genes was analyzed by reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. The value of the tlh genes was normalized by that of the his1 gene. Bars and error bars indicate mean and SEM of three or four experiments. A.U., arbitrary units.