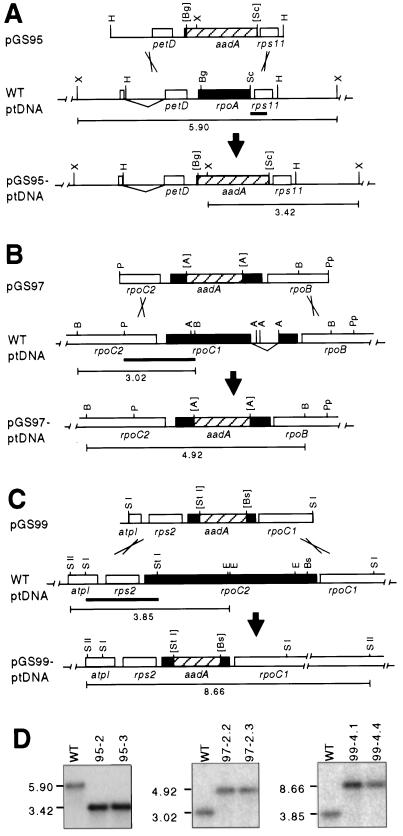
Figure 1.
Targeted deletion of rpo genes from the plastid genome. A, Deletion of the rpoA gene. Homologous recombination events (hatched lines) between ptDNA sequences in vector pGS95 and the tobacco plastid genome yields a genome lacking rpoA. Probes for Southern blots in D are marked with thick horizontal lines. Map position of the probed restriction fragments with size in kilobases is shown below the maps. aadA, Chimeric spectinomycin resistance gene (Svab and Maliga, 1993); rpoA, rpoB, rpoC1, and rpoC2, the plastid genes encoding the α-, β-, β′-, and β"-subunits of PEP, respectively; atpI, petD, rps2, and rps11, plastid genes (Shinozaki et al., 1986). Restriction endonuclease cleavage sites: H, HincII; X, XbaI; Bg, BglII; Sc, ScaI; P, PstI; B, BamHI; Pp, Psp1406I; A, AccI; SI, SacI; SII, SacII; StI, StuI; E, EcoRV; Bs, BsrGI. Brackets indicate restriction sites eliminated during cloning. B, Deletion of the rpoC1 gene. Homologous recombination events (crossed lines) between ptDNA sequences in vector pGS97 and the tobacco plastid genome yields a genome lacking rpoC1. C, Deletion of the rpoC2 gene. Homologous recombination events (crossed lines) between ptDNA sequences in vector pGS99 and the tobacco plastid genome yields a genome lacking rpoC2. D, Southern probing demonstrates a uniform population of transformed plastid genomes. Total cellular DNA was isolated from the leaves of plants transformed with plasmids pGS95 (targeting rpoA), pGS97 (targeting rpoC1), and pGS99 (targeting rpoC2), and from wild-type green leaves (WT). Data are shown for two independently transformed lines (pGS95-2, pGS95-3), or two plants derived from the same transformation event (pGS97-2.2, pGS97-2.3 and pGS99-4.1, pGS99-4.4).