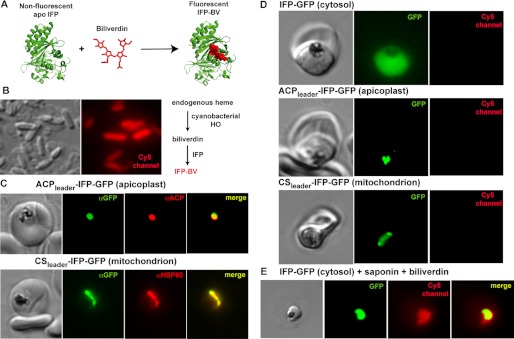
FIGURE 4.
Targeted episomal expression of a fluorescent biliverdin biosensor in P. falciparum parasites. A, unliganded and nonfluorescent IFP covalently binds free biliverdin to generate mature IFP-BV, whose fluorescence can be detected on the Cy5 channel. This scheme was constructed using the BV-bound x-ray structure of the D. radiodurans chromophore binding domain (Protein Data Bank code 3S7O), from which IFP is derived. B, heterologous co-expression of SynHO1 and IFP in E. coli enables in situ fluorescence detection of the BV product of SynHO1 within live bacteria imaged on the Cy5 channel of a fluorescence microscope. C, immunofluorescence microscopy of fixed parasites confirms apicoplast and mitochondrial targeting of episomally expressed IFP bearing a C-terminal GFP tag and the N-terminal leader sequence from either acyl carrier protein (ACP) or citrate synthase (CS), respectively. Parasites were stained with monoclonal αGFP and either a polyclonal αACP (apicoplast) or αHSP60 (mitochondrion) antibodies. The epitope recognized by the αACP antibody is distinct from the ACP leader sequence. D, fluorescence images of live parasites episomally expressing IFP within the parasite cytoplasm, apicoplast, or mitochondrion. E, fluorescence image of a live parasite expressing cytosolic IFP-GFP. The parasite was released from its host RBC via saponin treatment and incubated in exogenous biliverdin. Images on GFP and Cy5 channels were processed with identical brightness and contrast settings.