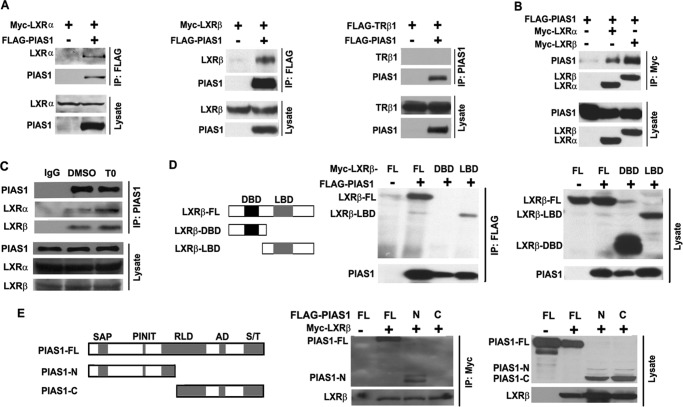
FIGURE 3.
PIAS1 interacts with LXRs. A and B, HEK 293T cells were co-transfected for 48 h with empty vector (−) or plasmids encoding FLAG-PIAS1, Myc-LXRα, Myc-LXRβ, or FLAG-TRβ1 as indicated. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-FLAG or anti-PIAS1 antibody (A) or with anti-Myc antibody (B). Immunoblotting was conducted using antibodies against FLAG or Myc. C, primary hepatocytes were treated with DMSO or T0901317 (T0) at 5 μm for 12 h. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with control IgG or anti-PIAS1 antibody. Immunoblotting was performed using antibodies against LXRα, LXRβ, or PIAS1. D, schematic diagram of the full-length (FL) and truncated versions of LXRβ analyzed for its association with PIAS1. DNA-binding domain (DBD), black box; ligand-binding domain (LBD), gray box. 293T cells were co-transfected with the indicated plasmids. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting were likewise performed as in A. E, schematic diagram of the full-length (FL) and truncated versions of PIAS1 analyzed for its interaction with LXRβ. The domain structure of PIAS1 is as follows: SAP domain (SAP), PINIT amino acid motif (PINIT), RING finger-like zinc-binding domain (RLD), highly acidic domain (AD), and serine- and threonine-rich region (S/T). 293T cells were co-transfected with the indicated plasmids. Immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting were likewise performed as in B. All results are representative of at least two independent experiments.