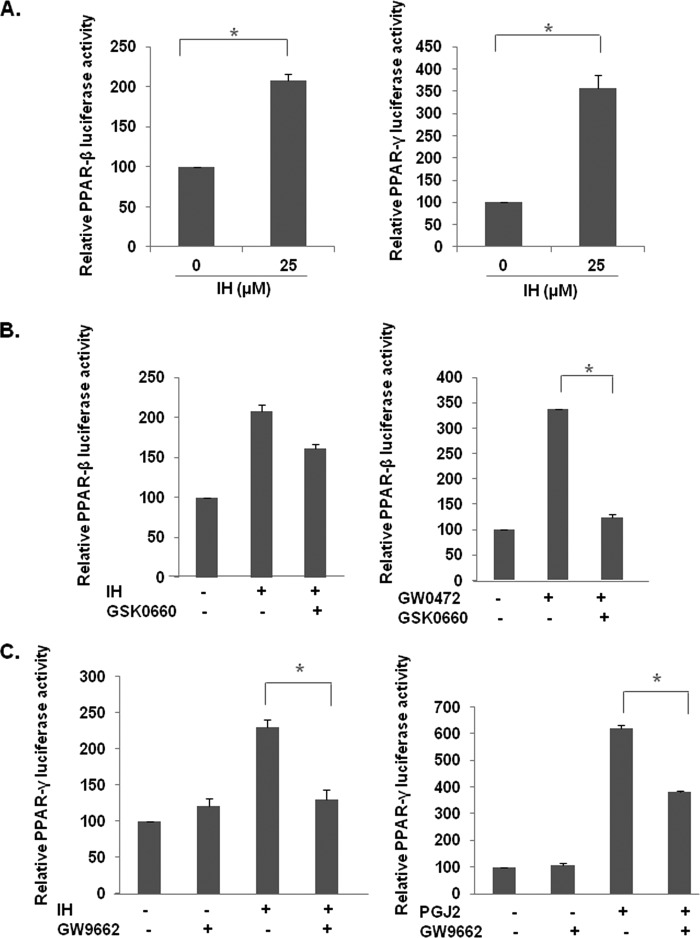
FIGURE 4.
Effect of IH PPAR activity in GC cells. A, effect of IH in PPARs. The cells were transfected with GAL4-PPAR-β/δ LBD and GAL4-PPAR-γ LBD plasmids, together with GAL4-Luc and β-gal plasmids for 4 h before treatment with 25 μm IH for 18 h. The data are expressed as percentages of the respective PPAR activity relative to the control. The values are the means ± S.E. of two or three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05. B, the inhibitor of PPAR-β/δ, GSK0660, could not block IH-induced PPAR-β/δ activity. The cells were transfected with GAL4-PPAR-β/δ LBD plasmids together with GAL4-Luc and β-gal plasmid for 4 h. The cells were pretreated with 50 μm GSK0660 for 4 h before treatment with 25 μm IH or 10 μm GW0742, a PPAR-β/δ agonist, both for 18 h. The data are expressed as percentages of the PPAR-β/δ activity relative to the control. The values are the means ± S.E. of two or three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05. C, IH-induced PPAR-γ activity could be blocked by GW9662, an inhibitor of PPAR-γ. The cells were transfected with GAL4-PPAR-γ LBD plasmids together with GAL4-Luc and β-gal plasmid for 4 h. The cells were pretreated with 10 μm or 20 μm GW9662 for 2 h before treatment with 25 μm IH or 20 μm PGJ2, a PPAR-γ agonist, both for 18 h. The data are expressed as percentages of the PPAR-γ activity relative to the control. The values are the means ± S.E. of two or three independent experiments. *, p < 0.05.