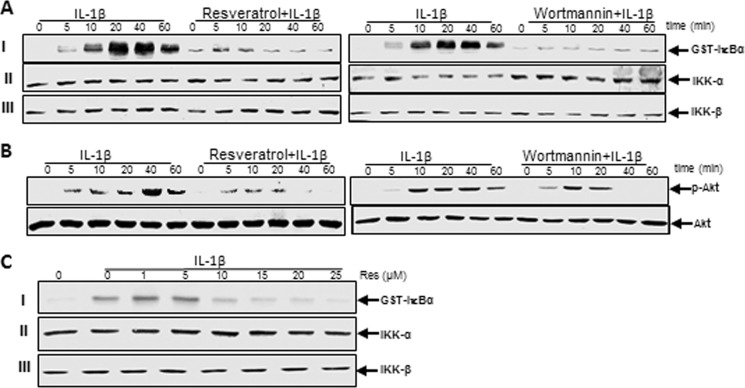
FIGURE 12.
Effects of resveratrol and PI3K inhibitor wortmannin on IL-1β-induced activation of IKK and Akt in human tenocytes. Serum-starved human tenocytes in monolayer culture were either treated with IL-1β alone for 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, or 60 min or were pretreated with resveratrol (5 μm) or wortmannin (10 nm) for 1 h and then co-treated with IL-1β for 0, 5, 10, 20, 40, or 60 min. A, to determine the activation level of IKK, whole cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with an antibody against IKK and underwent immune complex kinase assay as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Extracts were then fractionated on SDS-PAGE and examined by Western blot analysis using anti-IKK-α, anti-IKK-β, and anti-phosphospecific-IκBα antibodies. B, cell lysates from the same cells were also examined for phosphorylation of Akt by immunoblotting with antibodies against Akt and phosphospecific-Akt. C, shown is the direct effect of resveratrol treatment on IL-1β-induced IκB kinase activation. Serum-starved human tenocytes were treated with 10 ng/ml IL-1β. The cell extracts were prepared and immunoprecipitated with anti-IKK-α antibodies. The immunocomplex kinase assay was performed in the absence or presence of resveratrol at the indicated concentrations. Data shown are representative of three independent experiments.