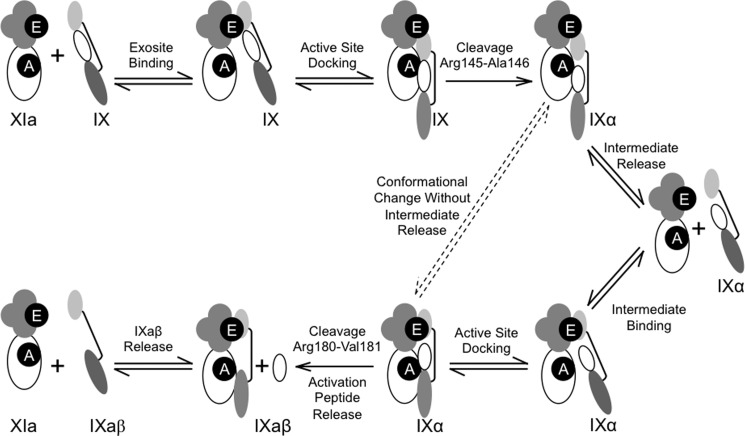
FIGURE 6.
Model for the mechanism of fIX activation by fXIa. In the schematic images representing fXIa, apple domains are shown as four clustered gray circles with the exosite on A3 indicated in black (E). The fXIa catalytic domain is a white ellipse with the active site indicated by a black circle (A). For fIX, the catalytic domain (dark gray ellipse) and light chain (light gray ellipse) are connected by a line representing a disulfide bond. The fIX activation peptide is the white oval between the heavy and light chains. Bi-directional arrows represent reversible binding, and uni-directional arrows represent proteolytic cleavage. FIX is activated by a fXIa subunit by sequential cleavage after Arg145 and Arg180, with the intermediate fIXα released and then rebound to the fXIa A3 domain. Details of the model are described in the text. The dashed lines indicate the possibility that some fraction of fIXα may be converted to fIXaβ without release from the fXIa A3 domain.