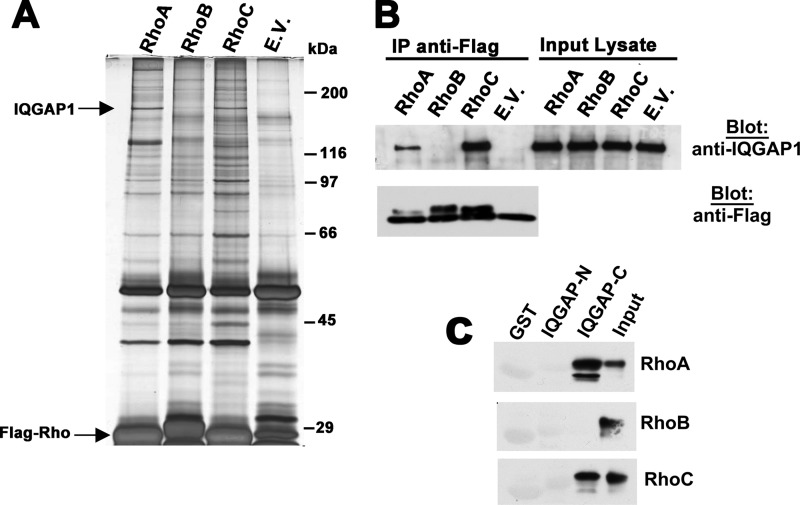
FIGURE 1.
IQGAP1 interacts with RhoA/C but not RhoB. A, 293T cells were transfected with expression vectors encoding Flag epitope-tagged, constitutively active RhoA, RhoB, and RhoC (each with a glycine to valine substitution at position 14), or empty vector (E.V.), and cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-Flag antibody. Precipitated proteins were eluted with Flag peptide and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/silver staining. Bands specifically associated with Rho A and C were excised, subjected to trypsin digestion, and analyzed by mass spectrometry. Bands migrating at ∼190 kDa were identified as IQGAP1. B, 293T cells were transfected with the same Rho constructs as in panel A, and anti-Flag immunoprecipitates were analyzed by Western blotting for the presence of endogenous IQGAP1 (top panel). A fraction of the immunoprecipitates was analyzed by blotting with anti-Flag antibody (bottom panel). C, N-terminal or C-terminal halves of IQGAP1 (IQGAP-N (amino acids 1–862) or IQGAP-C (amino acids 863–1657)) were expressed as GST-fusion proteins and purified from bacteria. Beads loaded with GST-IQGAP-N, IQGAP-C, or GST were incubated with Flag-tagged RhoAV14, RhoBV14, or RhoCV14 purified from 293T cells; beads were washed, and analyzed for the presence of RhoA, RhoB, or RhoC, respectively, with 10% input of each Rho protein shown in the last lane.