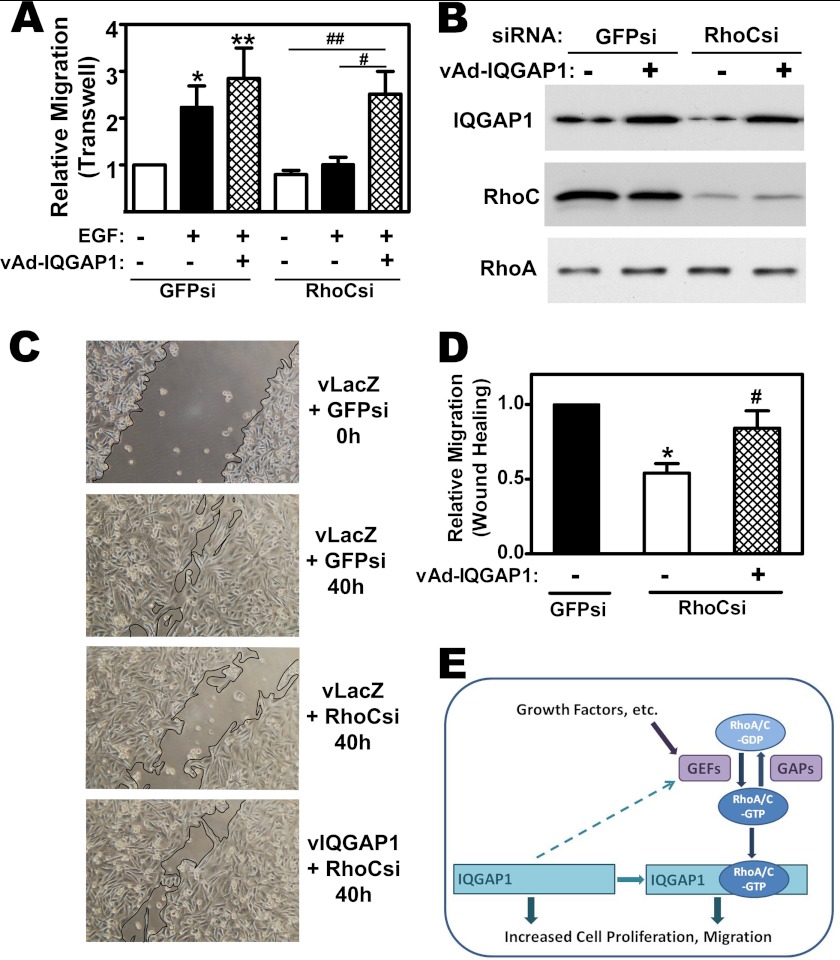
FIGURE 8.
IQGAP1 can restore migration in RhoC-depleted cells; IQGAP1 functions both upstream and downstream of RhoA and C. A, MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with siRNAs specific for GFP or RhoC, and infected with adenovirus encoding LacZ or IQGAP1; cell migration was measured as in Fig. 7A, with some cells receiving EGF in the lower chamber (*, p < 0.05 or **, p < 0.01 for the comparison to control; #, p < 0.05 or ##, p < 0.01 for the comparison between LacZ and IQGAP1 virus in RhoC siRNA-transfected cells). B, cells were treated as in A, and cell lysates were analyzed by Western blotting with antibodies specific for IQGAP1 (top), RhoC (middle), or RhoA (bottom panel). C, cells were siRNA transfected and infected with virus encoding LacZ (vLacZ) or IQGAP1 (vIQGAP1) as in panel A, but migration was measured in a wound-closure assay, with photographs taken immediately, and 40 h after cells were scratched off the plate. D, summary of three experiments performed as in C; the number of cells migrating into the wound in the control culture (GFP siRNA-transfected and LacZ virus-infected) was assigned a value of one (*, p < 0.05 for the comparison to control; #, p < 0.05 for the comparison between LacZ and IQGAP1 virus in RhoC siRNA-transfected cells). E, model depicting IQGAP1 binding GTP-bound RhoA/C and mediating RhoA and RhoC-induced DNA synthesis and migration, respectively. The activation state of RhoA/C is regulated by GEFs and GAPs; growth factors stimulate GEFs, and IQGAP1 appears to enhance Rho activation by GEFs. Interaction of RhoA/C-GDP with Rho guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors is not shown in this figure. IQGAP1 has no intrinsic GAP activity, and IQGAP1 overexpression leads to increased cell proliferation and migration through RhoA/C-independent mechanisms.