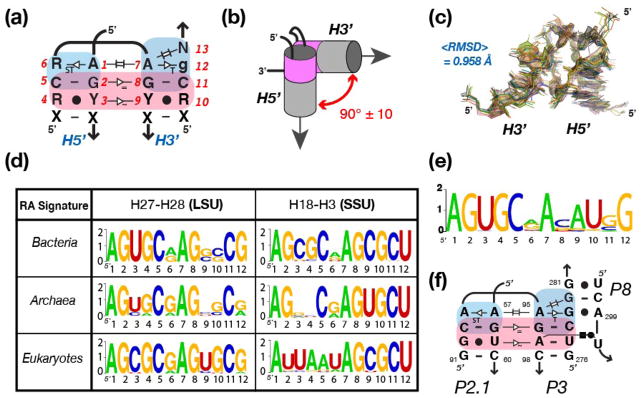
Figure 1.
Definition and structural characteristics of the RA motif. (a) Nomenclature and generic sequence signature based on the structural analysis of RA motifs from known X-ray structures (listed in Supporting Information, Table S1). Nucleotides (nt) positions have been numbered from 1 to 13 to facilitate comparison. Tertiary interactions and non-canonical base pairs (bp) are indicated on the 2D diagram according to previously defined nomenclature. The regions colored in blue and pink highlight the “GA-minor” and “along groove” components of the RA motif, respectively. R and Y stand for purine and pyrimidine, respectively; N stands for any nucleotide; X stands for any nucleotide involved in WC:WC bp; lower case nucleotides are less conserved than upper case nucleotides. (b) Topological characteristics of the RA motif. The two adjacent helices H5′ and H3′ are oriented by 90° similarly to the corners of a log cabin. Position N13 at the 3′ end of the motif is in perfect helical continuity with H3′, allowing an additional helix to be stacked in continuity of this helix as previously demonstrated 21. (c) Superposition and RMSD of the ribose-phosphate backbone of RA motifs from known X-ray ribosomal structures (see Supporting Information, Table S1). (d) Sequence signatures corresponding to RA motifs identified at two distinct locations in the 23S and 16S rRNA sequences of Bacteria, Archaea and Eukaryotes. The sequence signatures were obtained by comparative sequence analysis of non-redundant 23S and 16S rRNA sequence obtained from the European Ribosomal RNA Database 52–55. The sequence space is represented as WebLogo (http://weblogo.berkeley.edu/) 58,59, where the x-axis corresponds to nucleotide positions (as indicated in Figure 1a) and the y-axis corresponds to bits. The larger the letter is, the more conserved it is. (e) Sequence signature of the RA motif at the P2.1-P3 junction determined from 51 group IC1 and ID intron sequences 41. (f) 2D-diagram of the P2.1-P3-P8 RA junction from the Tetrahymena ribozyme with proposed tertiary interactions. Numbering is according to the one of the Tetrahymena group IC1 ribozyme 46.