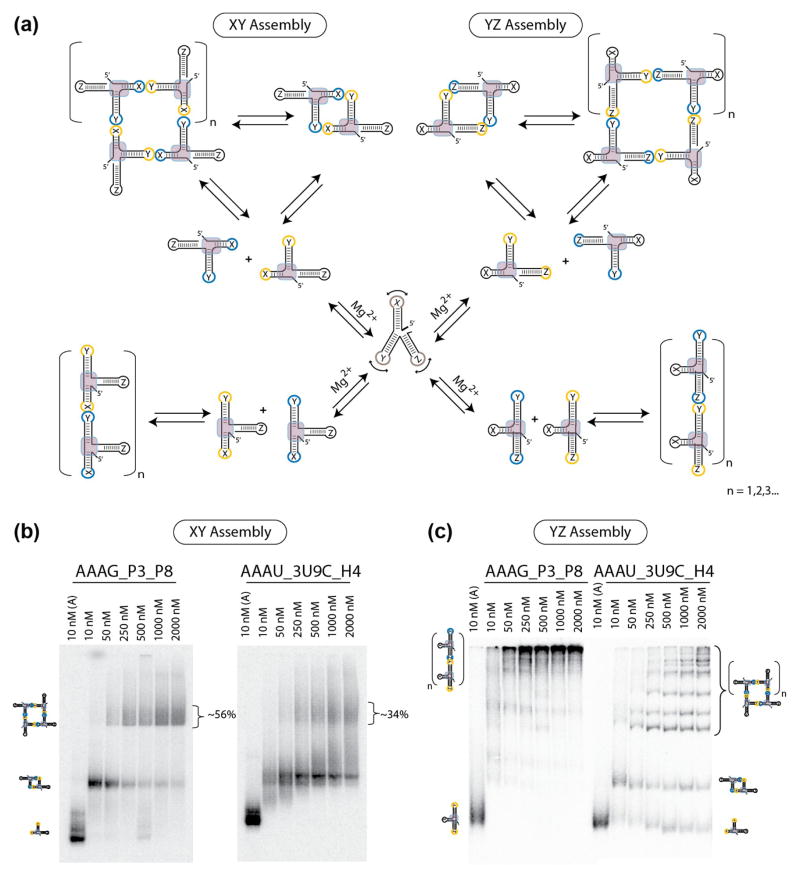
Figure 4.
Monitoring the topology of the P2.1-P3-P8 junction of group I introns and H3-H4-H18 domain of bacterial 16S rRNA by supra-molecular assembly. (a) Schematic illustrating the experimental design and self-assembly strategy used to test expanded RA variants based on XY assembling interface (left) and YZ assembling interface (right). To monitor assembly under the control of the RA motif (left), HIV kissing-loops were placed at the ends of stems X and Y. To monitor assembly under the control of the topology of the stem Y with respect to stem Z, HIV kissing-loops were placed at the ends of the stems Y and Z. (b) Native PAGE gel-shift assays (1x TB at 2mM Mg2+ and 10°C) demonstrate the ability of the AAAG_P3_P8 and AAAU_3U9C_H4 constructs to form tectosquares by XY assembly. (c) Native PAGE gel-shift assays (1x TB at 2mM Mg2+ and 10°C) demonstrate by YZ assembly that stems Y and Z adopt a topology in the group I intron junction (AAAG_P3_P8) that is distinct from the one in the H3-H4-H18 domain from 16S rRNA (AAAU_3U9C_H4).