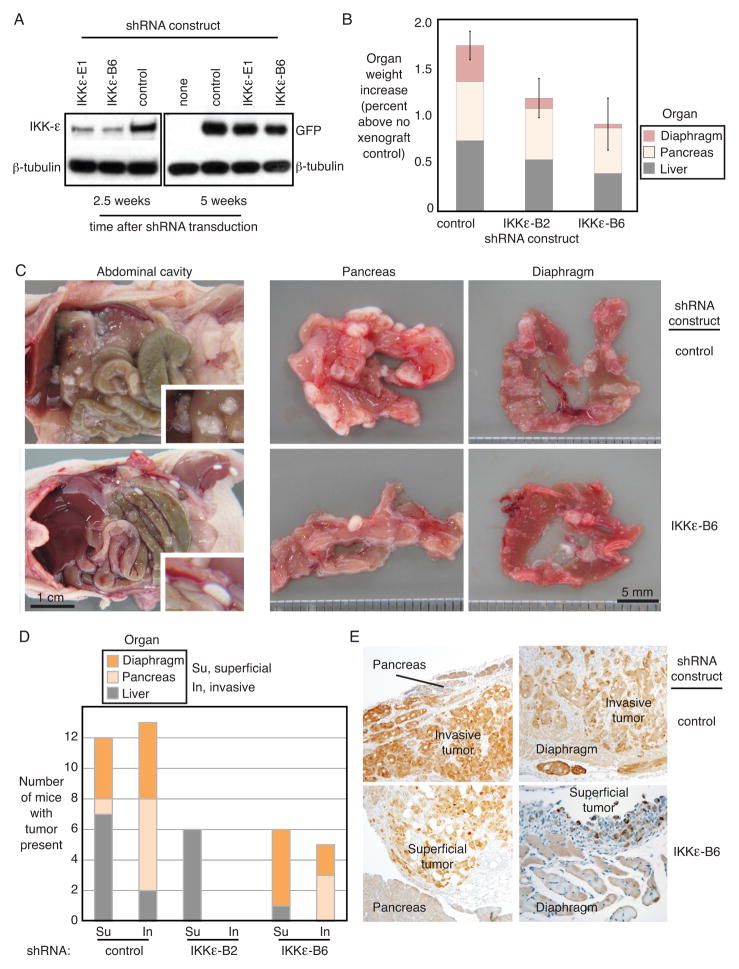
Figure 5. IKKε promotes tumor growth, invasion and metastasis in vivo.
(A) Persistent integration of the shRNA construct in Ovcar8 cells over the time course of mouse xenograft experiments was confirmed by Western blot of IKKε protein (2.5 weeks) and co-expressed GFP (5 weeks). β-tubulin was a loading control. (B) Organ weight was measured in mice after necropsy. Shown are the average organ weights for diaphragm, pancreas and liver (Ovcar5 xenografts, n=9 each). Organ weight is expressed as percent body weight, increased over organs from non-xenograft controls (PBS injected intraperitoneally). Error bars represent S.E. (C) Gross anatomical examination of the abdominal cavity showed decreased adhesion to external organ surfaces in IKKε-depleted Ovcar8 xenografts (left panels). Tumor adherence to pancreas and diaphragm also appeared decreased (right panels). (D) Quantification of xenograft invasion into secondary organs showed decreased invasiveness of Ovcar5 cells depleted of IKKε by either of the shRNA constructs. Shown is the number of animals with tumor present in each organ. (E) Immunohistochemical analysis of tissues exhibiting Ovcar5 xenografts, stained for GFP as a marker of shRNA construct integration. GFP protein is shown by the brown immunohistochemical stain, at 10X magnification.