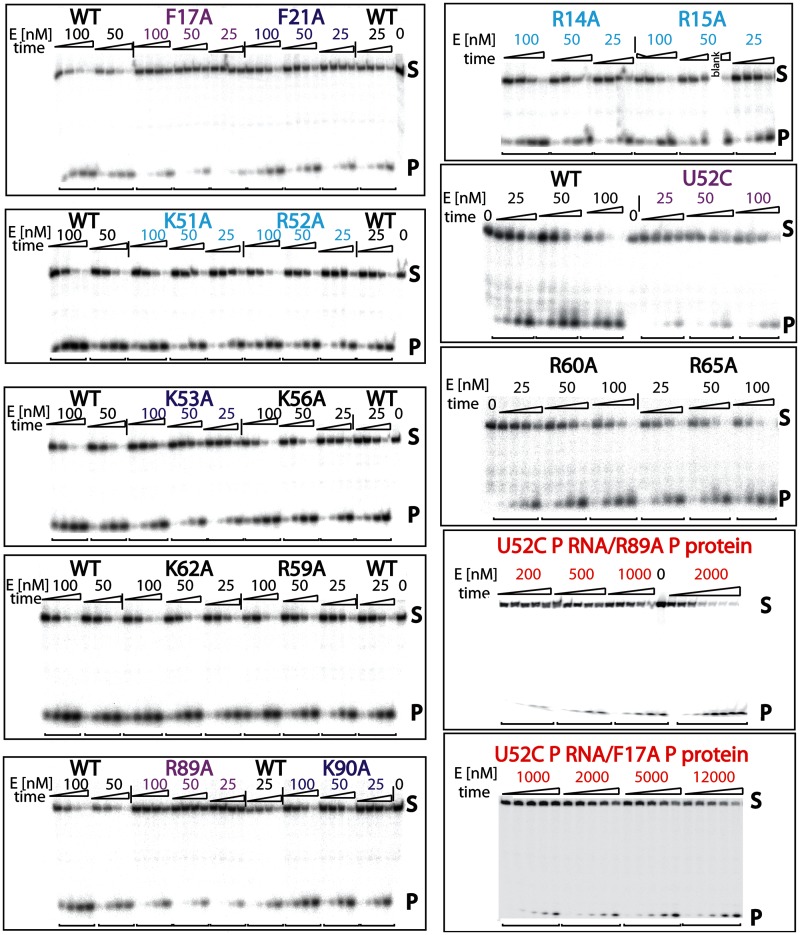
Figure 2.
Representative cleavage kinetics of pre-tRNA catalyzed by the wild-type and mutant T. maritima RNase P holoenzymes. Multiple time course reactions (time points: 0.25, 1, 4 and 16 min) at different enzyme concentrations enabled the quantitative measurement of single-turnover reaction kinetic parameters (kcat/KM) (Table I). In most cases, enzyme concentrations (25, 50, 100 and 200 nM) fell within the linear range, enabling extraction of kcat/KM from a plot of [E] versus kobs (see ‘Materials and Methods’ section and Supplementary Figure S3). In other cases, such as the double mutants (dm) U52C RNA/F17A protein or U52C RNA/R89A P protein (red), high holoenzyme concentrations (200–12000 nM) were required to observe the formation of any product. In addition, the P RNA ribozyme by itself (under high and medium divalent/monovalent conditions), as well as R89A, F17A and U52C P RNA mutants, were tested at higher enzyme concentrations (vide supra and Supplementary Figure S3). Compared with the wild-type T. maritima RNase P holoenzyme (black), point mutants range from showing no or little effect (black (K56A, R59A, R60A, K62A and R65A)), to modest (light blue (R14A, R15A, K51A, R52A)), substantial (dark blue (F21A, K53A, R90A)), severe (magenta (U52C P RNA, R89A and F17A)) and deleterious (red, dm U52C RNA/F17A protein or U52C RNA/R89A P protein) effects on catalytic activity.