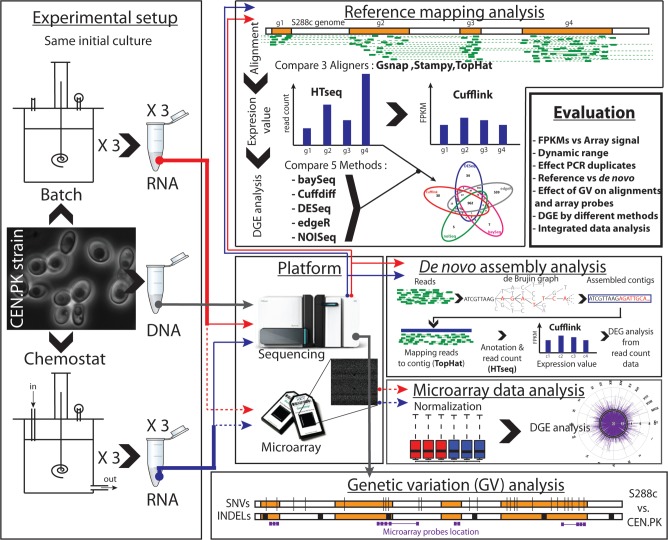
Figure 1.
Study design overview. The same initial culture of S. cerevisiae strain CEN.PK-113-7D was used for DNA-seq (gray line) and transcriptome analysis to reduce technical variation and polymorphism. The strain was cultivated under two different metabolic conditions, in well controlled batch (red line) and chemostat (blue line) fermentation. From the triplicates’ cultures, samples for extraction of DNA and RNA were extracted. The extracted RNA was used, in parallel, for microarray analysis through Affymetrix platform (dash lines) and for RNA-seq (solid line). DNA-seq and RNA-seq were performed with the Illumina platform. DNA-seq data were used to identify the genetic variation (SNVs and indels) between the strain CEN.PK 113-7D and the reference strain S288 and to identify genetic variations in the microarray probes. The RNA-seq data were analyzed with the reference mapping approach and de novo assembly approach. The results obtained with different methods were compared and cross-compared with the results from microarray analysis.