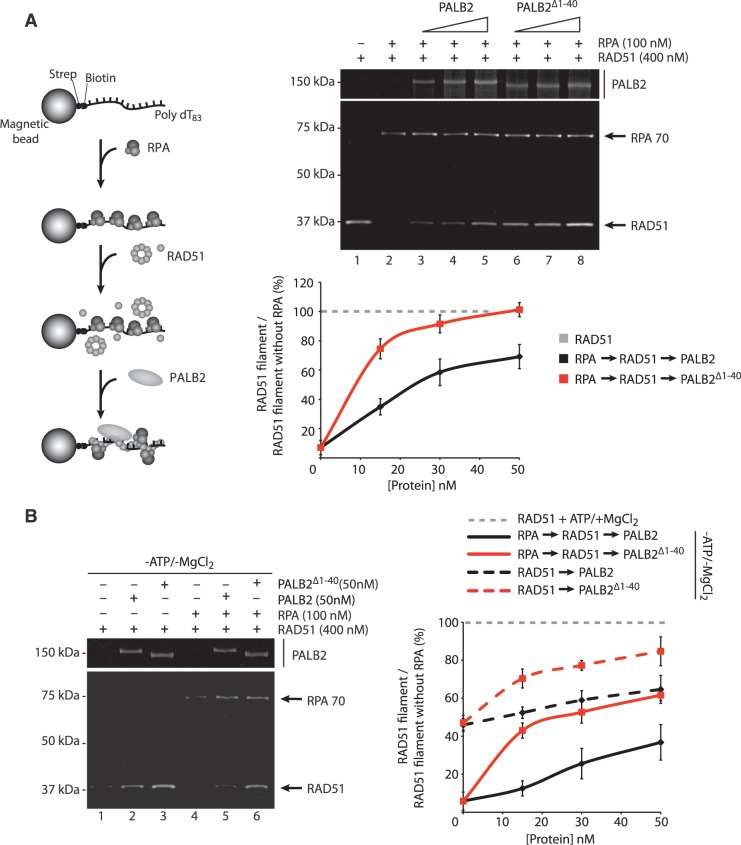
Figure 3.
Stimulation of RAD51 filament formation by monomeric PALB2. (A) Left: schematic of RPA displacement assay. Right: RPA bound to a ssDNA oligonucleotide prevents RAD51 assembly (lane 2) whereas addition of PALB2 or PALB2Δ1–40 (15, 30 and 50 nM) stimulates RAD51 filament formation in presence of RPA (lanes 3–8). Bottom: quantification of the results. The Y-axis represents the ratio between the values obtained for RAD51 filament in the presence of RPA and PALB2 or PALB2Δ1–40 divided by the value obtained for RAD51 filament with ATP and magnesium without RPA (set at 100%). (B) Left: RPA displacement assay in the absence of ATP and MgCl2. Right: quantification of the results. The Y-axis represents the ratio between the values obtained for RAD51 filament in the absence of ATP/MgCl2 with or without RPA and PALB2 or PALB2Δ1–40 divided by the value obtained for RAD51 filament with ATP and magnesium without RPA (set at 100%).