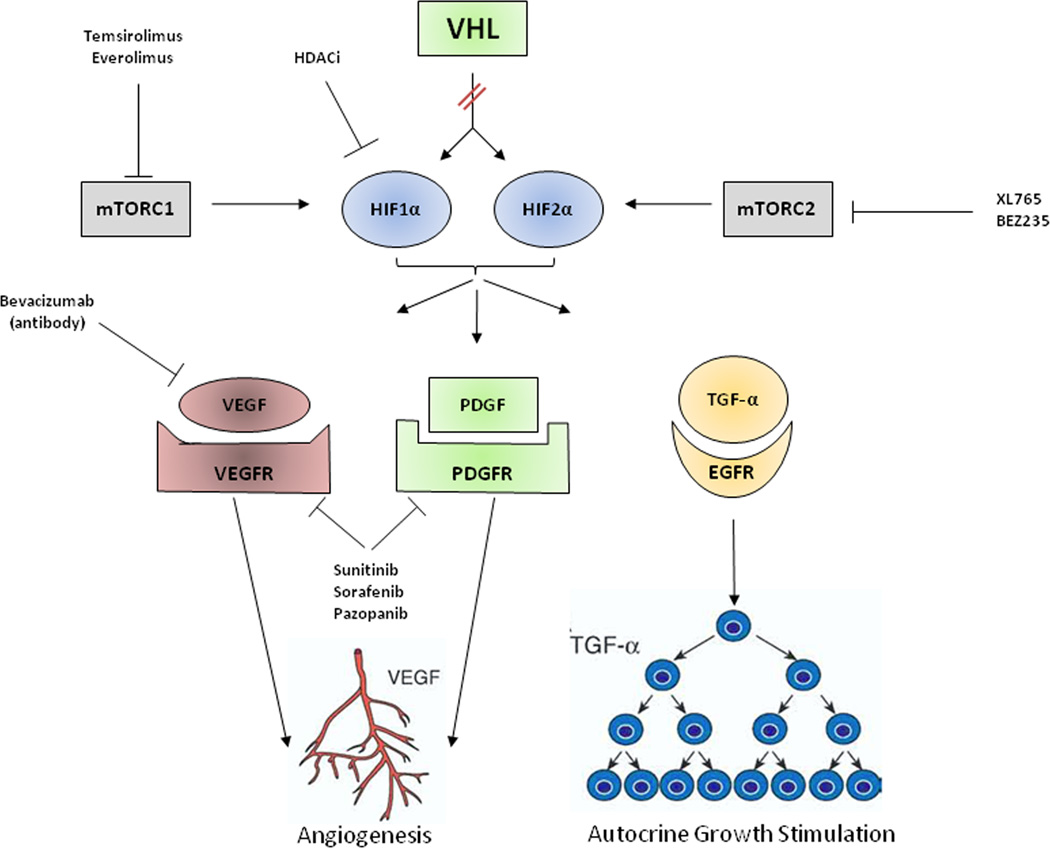
Figure 1. Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma Pathways and Targeted Therapies.
The VHL gene is mutated in the majority of sporadic clear cell kidney cancer. As a result of mutation, the VHL protein cannot target and degrade hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) 1 α /2α. HIF overaccumulates and causes increased transcription of downstream genes, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) and transforming growth factor alpha (TGF-α).
Current therapeutic approaches include antibodies, such as bevacizumab, that targets VEGF, tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as sunitinib, sorafenib, and pazopanib that target the VEGF and PDGF receptors and rapalogues such as temsirolimus and everolimus that target the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1).
Future approaches could include agents that target HIF directly including histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) and indirectly via inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 (mTORC2).