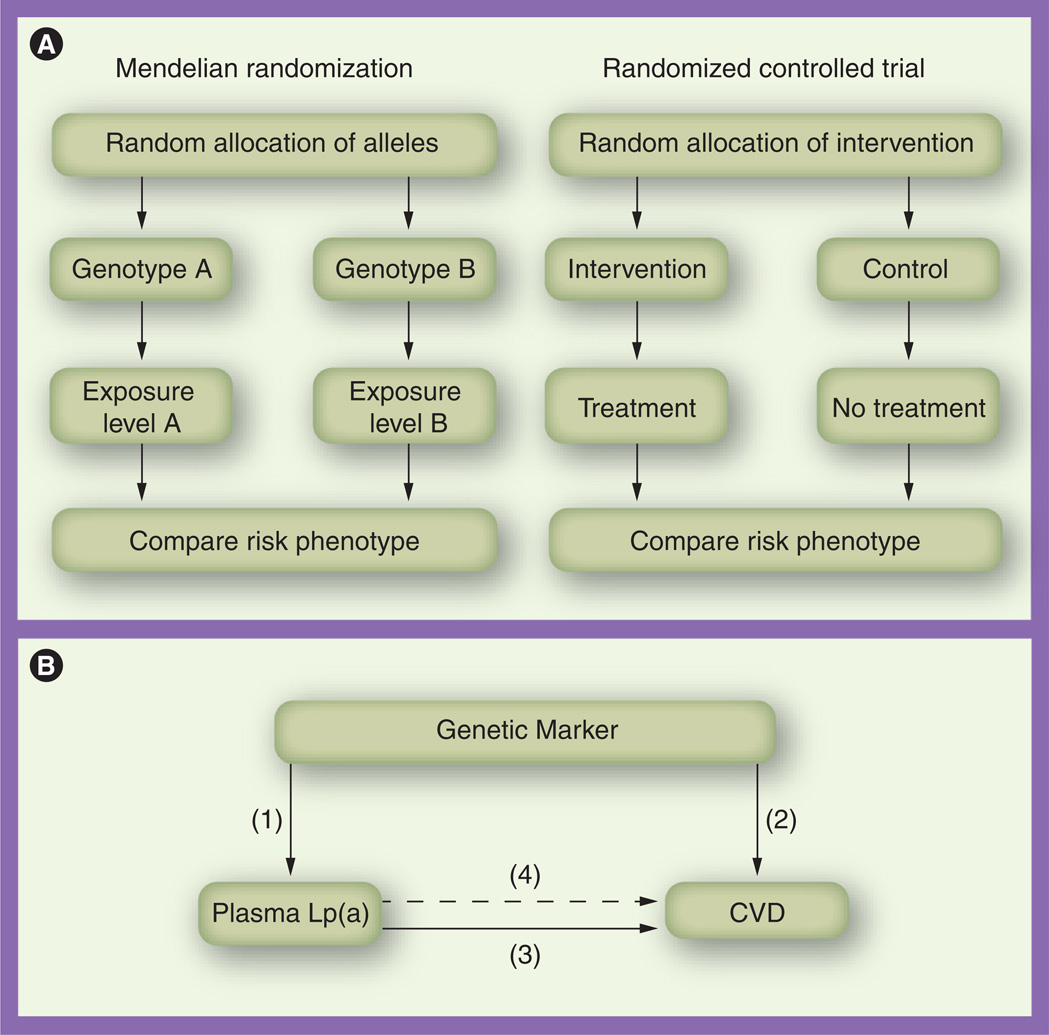
Figure 2. Mendelian randomization and randomized controlled trial in the case of lipoprotein(a) and cardiovascular disease.
(A) Parallel relationship between Mendelian randomization and randomized controlled trial. (B) Application of Mendelian randomization to the case of Lp(a) and CVD. Relationships include (1) genetic marker and plasma Lp(a) levels; (2) genetic marker and CVD risk; (3) plasma Lp(a) levels and CVD risk; and (4) the predicted relationship between genetically elevated Lp(a) levels and CVD risk (derived from the first two estimates), which is then compared with the observed estimate (3).
CVD: Cardiovascular disease; Lp(a): Lipoprotein(a).
Modified with permission from [65].