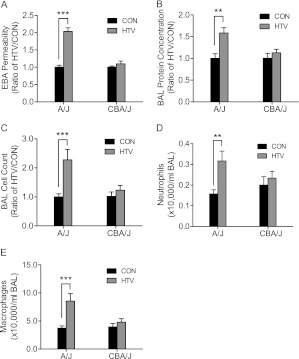
Figure 3.
Lung injury increased in sensitive A/J mice after HTV ventilation as compared with resistant CBA/J mice. (A) EBA permeability increased in sensitive A/J mice compared with CON, whereas HTV did not increase EBA permeability in resistant CBA/J mice after 4 hours of mechanical ventilation. Values are means (±SEM) (four to six mice/group). (B) HTV increased bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) protein concentration in sensitive A/J mice, whereas it failed to increase BAL protein concentration in resistant CBA/J mice after exposing them to 4 hours of mechanical ventilation compared with CON. Values are means (±SEM) (four to six mice/group). (C) HTV increased BAL total cell number counts in sensitive A/J mice compared with CON after 4 hours, whereas HTV did not increase BAL total cell number counts in resistant CBA/J mice. (D) HTV increased BAL neutrophils in sensitive A/J mice compared with CON after 4 hours, whereas HTV did not increase BAL neutrophil counts in resistant CBA/J mice. (E) HTV increased BAL macrophages in sensitive A/J mice after 4 hours of HTV compared with CON. Values are means (±SEM) (four to six mice/group). Significant difference from control (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001), as determined by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons.