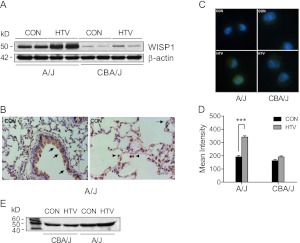
Figure 4.
Mechanical ventilation increased WISP1 protein in sensitive A/J mice. (A) HTV ventilation increased WISP1 protein level in lung tissues determined by immunoblot in sensitive A/J mice, whereas there was no change in WISP1 levels in resistant CBA/J mice exposed to 4 hours of HTV. β-actin was the loading control. Data are representative of three tests. (B) Immunohistochemistry of WISP1 protein in CON mice from the sensitive A/J strain. The localization of WISP1 protein was similarly detected in airway and alveolar epithelium (arrow) and alveolar macrophages (arrowhead) in both sensitive A/J and resistant CBA/J strains after CON and HTV. Data shown are representative of two tests. (C) Immunofluorescence staining for WISP1 protein (Alexa-488 fluorescently labeled antibody, green color) in alveolar macrophages increased more in sensitive A/J mice than in resistant CBA/J mice after HTV. (D) The mean fluorescence intensity for WISP1 immunostaining was determined by quantifying fluorescent intensity of 10–20 cells in 4–5 fields that were randomly selected with Nikon image software NIS-Element AR 3.2. Values are means (±SEM). Significant difference from control (***P < 0.001), as determined by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons. (E) Immunoblot of WISP1 protein in BAL fluid was elevated after 4 hours of HTV in the sensitive A/J strain compared with the resistant CBA/J strain.