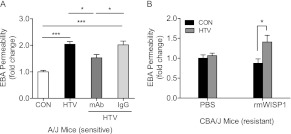
Figure 5.
Anti-WISP1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) or recombinant mouse WISP1 protein (rmWISP1) reversed phenotype to VILI in sensitive A/J mice or resistant CBA/J mice, respectively. (A) A/J mice were intratracheally administered anti-WISP1 mAb or serum IgG (0.5 μg/g in 50 μl PBS) using a MicroSpray syringe before HTV mechanical ventilation. Lung injury was evaluated by measuring EBA permeability after 4 hours of HTV or CON. Anti-WISP1 mAb decreased EBA permeability after 4 hours of HTV-induced lung injury in sensitive A/J mice, whereas serum IgG did not decrease lung injury. Values are means (±SEM) (four to six mice/group). Significant difference from control (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001), as determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post test. (B) CBA/J mice were intratracheally instilled with rmWISP1 (0.5 μg/g in 50 μl PBS) or 50 μl PBS as a control using a MicroSpray syringe before HTV mechanical ventilation or CON. Values are means (±SEM) (n = four to six mice/group). Significant difference from control (*P < 0.05), as determined by two-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons.