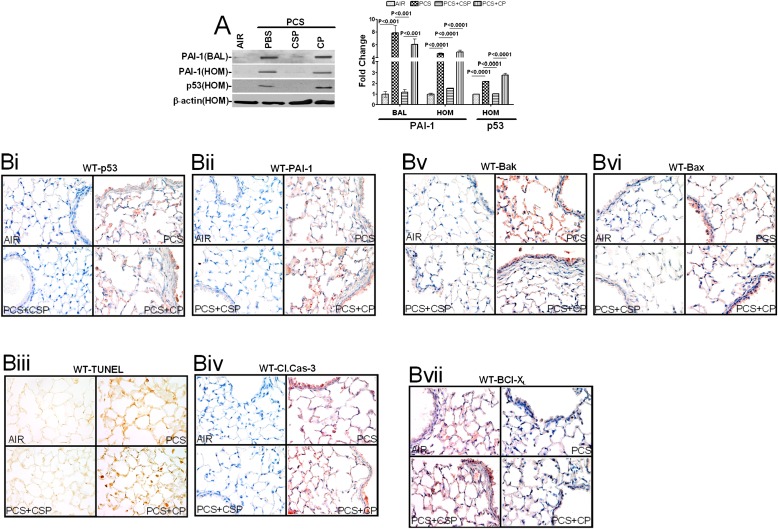
Figure 4.
CSP treatment inhibits CS-induced p53 and PAI-1 expressions and apoptosis in wild-type (WT) mouse lung epithelial cells. (A) BAL fluid and lung homogenates (HOM) from mice (n = 5 per group) exposed to ambient air or passive CS for 20 weeks in the presence or absence of CSP or CP were immunoblotted for the changes in PAI-1 and p53 expressions. Membranes containing proteins from the lung homogenates were stripped and analyzed for β-actin to assess equal loading. The fold change in PAI-1 is presented as a bar graph based on densities of individual bands in the BAL fluid under various treatment conditions versus PBS controls. Individual bar represents fold changes in p53, and PAI-1 expression versus air control is shown as a bar graph. (B) Lung sections of WT mice as described in Figure 4A were subjected to immunohistochemical analyses for p53 (Bi) or PAI-1 (Bii), TUNEL staining (Biii), active Caspase-3 (Biv), Bak (Bv), Bax (Bvi), and Bcl-XL (Bvii) to assess changes in the expressions of p53, PAI-1, and pro-apoptotic and anti-apoptotic proteins as well as apoptosis in situ. Experiments were repeated at least three times, and representative results are illustrated.