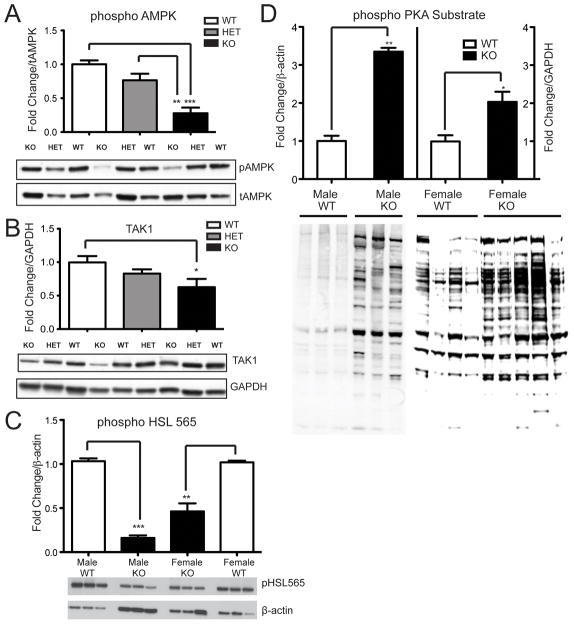
Figure 3. Phospho-AMPK, TAK1, and phospho-HSL (ser565) levels are decreased and PKA substrate phosphorylation is increased in VGF knockout WAT.
Phospho− AMPK (panel A), TAK1 (panel B), and phospho− HSL (ser565) (panel C) protein levels in gonadal WAT from Vgf +/Vgf+, Vgf+/Vgf−, and Vgf−/Vgf− mice were determined by western blotting, densitometry, and quantification using NIH image. Results were normalized to total AMPK (panel A), GAPDH (panel B), and β-actin (panels C and D). VGF ablation significantly decreased AMPK phosphorylation, TAK1 levels, and HSL (ser565) phosphorylation, in Vgf−/Vgf− compared to Vgf+/Vgf+ WAT [n=5−6 mice of each genotype per group, mean ± SEM; ***p = 0.0001; **p = 0.0053 (panel A), **p = 0.0039 (panel C); *p = 0.0207, ANOVA and Tukey’s multiples comparison]. In panel D, phosphorylation of PKA substrate in epididymal/gonadal WAT tissue from male and female Vgf−/Vgf− (n=3 males and 5 females per group) and Vgf+/Vgf+ (n=3 males and 4 females per group) mice was measured by western analysis. Values are mean ± SEM relative to the Vgf+/Vgf+ control, normalized to β-actin. A significant increase in PKA substrate phosphorylation was noted (**p = 0.0072, *p = 0.0167) in male and female Vgf−/Vgf− WAT.