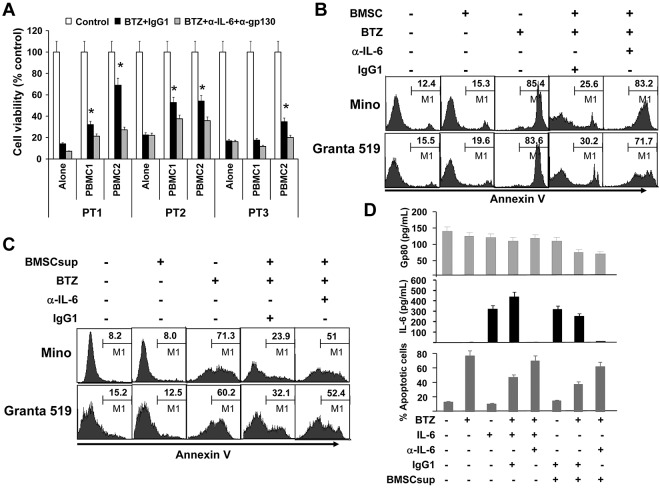
Figure 3.
Paracrine or exogenous IL-6 protects MCL cells against chemotherapy drug–induced apoptosis. (A) Viability of freshly isolated primary MCL cells from 3 patients (PT1-PT3) cocultured for 24 hours with PBMCs from 2 blood donors (PBMC1 and PBMC2) in Transwell inserts in the presence of BTZ (10nM) with the addition of IL-6–neutralizing (α-IL-6; 50 μg/mL) and gp130-blocking (α-gp130; 5 μg/mL) antibodies or control IgG1. After the culture, PBMCs in Transwell inserts were removed and MCL cells in the culture wells were subjected to MTS assay (*P < .05; compared with culture alone). Flow cytometry analysis showing the percentages of apoptotic Mino and Granta 519 cells in (B) culture alone or coculture with BMSCs (as a source of exogenous IL-6; cultured BMSCs secreted around 6000 pg/mL of IL-6) at a ratio of 1:300 of BMSCs:MCL cells in the presence or absence of BTZ (10nM) and IL-6–neutralizing antibodies (α-IL-6; 50 μg/mL) or control IgG1; or (C) cultures with or without the addition of BMSCsup (1000-fold diluted, as a source of IL-6) in the presence or absence of BTZ (10 nM) and IL-6-neutralizing antibodies (α-IL-6; 50 μg/mL) or control IgG1. Cell apoptosis was examined by Annexin V–binding assay. (D) Levels of gp80 and IL-6, and percentages of apoptotic MCL cells in cultures of Mino cells, with or without the addition of BMSCsup (1000-fold diluted, as a source of IL-6) in the presence or absence of BTZ (10nM), exogenous IL-6 (0.5 ng/mL), IL-6–neutralizing antibodies (α-IL-6; 50 μg/mL), or control IgG1. Cells were cultured as indicated previously for 48 hours and analyzed for apoptosis by annexin V–binding assay. Culture supernatants were collected and assayed by ELISA for gp80 and IL-8 secreted by MCL cells or provided as BMSCsup or added IL-6. Results of 3 independent experiments are shown.