Abstract
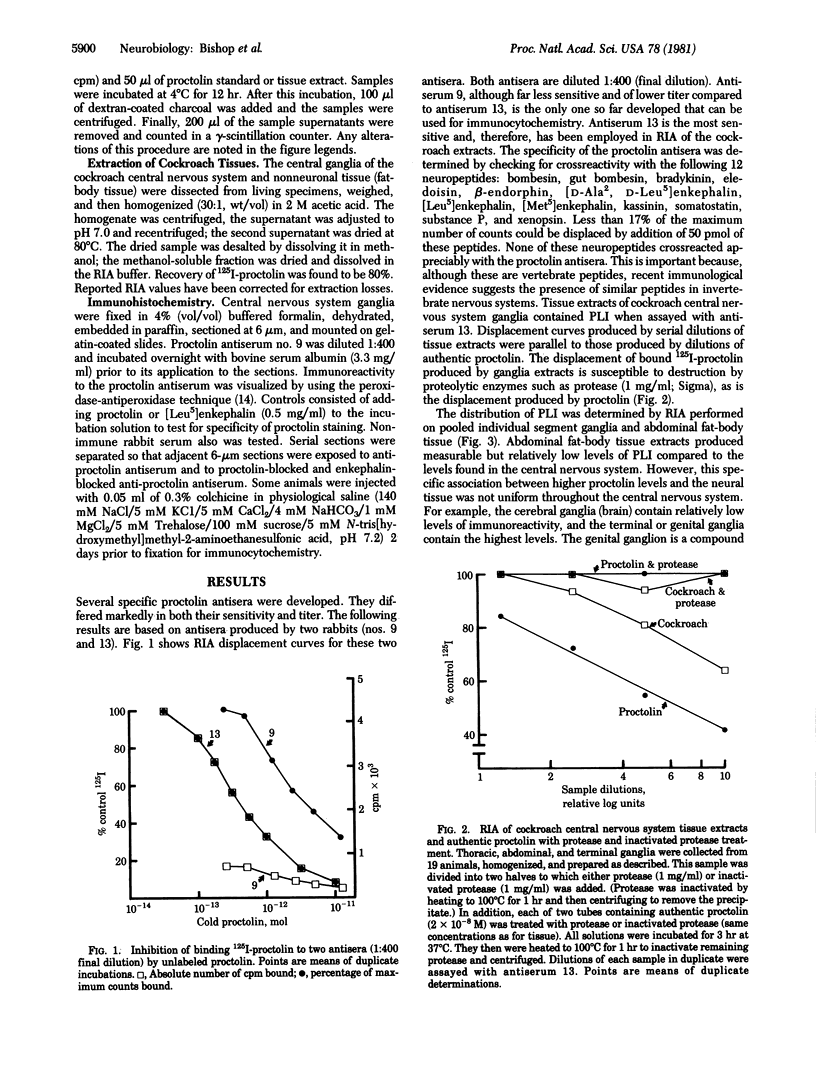
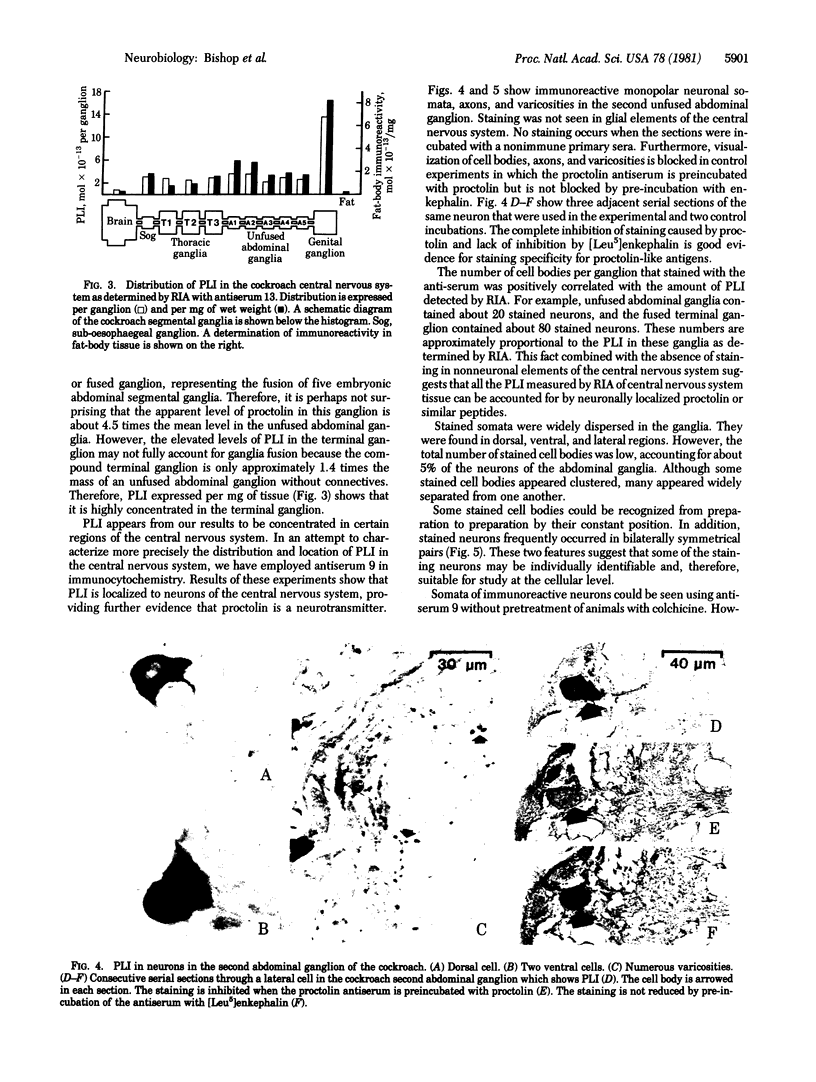
Proctolin (H-Arg-Tyr-Leu-Pro-Thr-OH) is a pentapeptide first extracted from cockroaches. It is known to have many neurohormonal effects and has been associated with specific, identified cockroach neurons. We have produced proctolin antisera and report here on their application in detecting proctolin-like immunoreactivity (PLI) in the cockroach central nervous system. Radioimmunoassay, capable of detectable 50 fmol of proctolin, was used to quantify the distribution of PLI. Highest concentrations were detected in the genital ganglia and lowest in the cerebral ganglia. Immunohistochemistry on the cockroach central nervous system demonstrated that PLI is localized to neurons. Neurons stained by using immunohistochemistry were widespread in the ganglia. Cell bodies were found to be in constant positions from animal to animal and to occur in bilaterally symmetrical pairs. These neurons are potentially identifiable.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alumets J., Hàkanson R., Sundler F., Thorell J. Neuronal localisation of immunoreactive enkephalin and beta-endorphin in the earthworm. Nature. 1979 Jun 28;279(5716):805–806. doi: 10.1038/279805a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson J. A., Sullivan R. E., Watson W. H., 3rd, Augustine G. J., Jr The neuropeptide proctolin acts directly on Limulus cardiac muscle to increase the amplitude of contraction. Brain Res. 1981 Jun 1;213(2):449–454. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90252-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown B. E. Proctolin: a peptide transmitter candidate in insects. Life Sci. 1975 Oct 15;17(8):1241–1252. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90133-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Ljungdahl A., Lundberg J. M., Schultzberg M. Peptidergic neurones. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):515–521. doi: 10.1038/284515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea M., Adams M. E. Pentapeptide (proctolin) associated with an identified neuron. Science. 1981 Jul 31;213(4507):567–569. doi: 10.1126/science.6113690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz T. L., Harris-Warrick R. M., Glusman S., Kravitz E. A. A peptide action in a lobster neuromuscular preparation. J Neurobiol. 1980 Nov;11(6):623–628. doi: 10.1002/neu.480110611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Brain peptides as neurotransmitters. Science. 1980 Aug 29;209(4460):976–983. doi: 10.1126/science.6157191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Starratt A. N., Brown B. E. Structure of the pentapeptide proctolin, a proposed neurotransmitter in insects. Life Sci. 1975 Oct 15;17(8):1253–1256. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90134-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaab D. F., Pool C. W., Nijveldt F. Immunofluorescence of vasopressin and oxytocin in the rat hypothalamo-neurohypophypopseal system. J Neural Transm. 1975;36(3-4):195–215. doi: 10.1007/BF01253126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zipser B. Identification of specific leech neurones immunoreactive to enkephalin. Nature. 1980 Feb 28;283(5750):857–858. doi: 10.1038/283857a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




