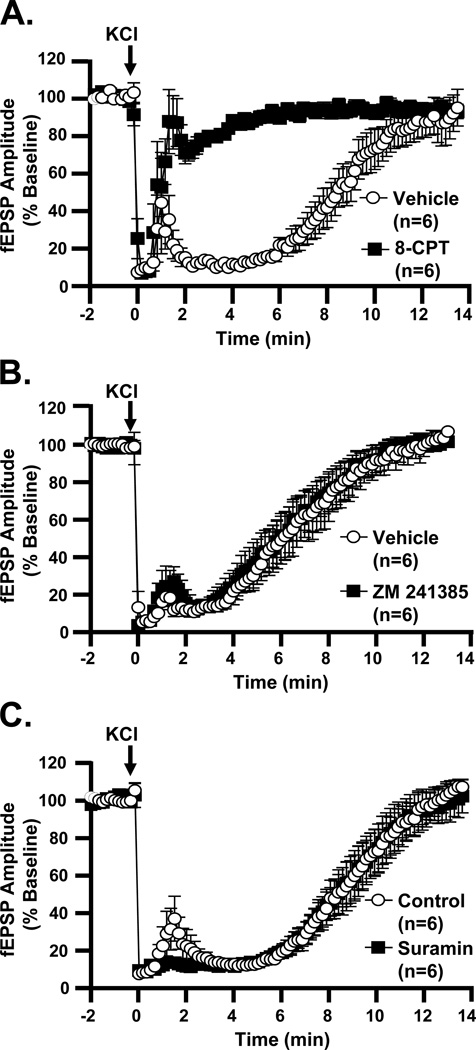
Figure 8. A1R antagonist, but not other purinergic receptor antagonists, abolishes secondary phase of synaptic depression after SD.
A: The A1R antagonist 8-CPT (10 µM) accelerates recovery of fEPSPs after SD, by comparison with interleaved vehicle-treated slices (t50 0.6±0.1 vs. 8.1±0.7 min, 8-CPT vs. vehicle, p<0.0001, unpaired t-test). B: Recovery of fEPSP amplitudes in the A2AR antagonist ZM 241385 (500 nM) closely matches that in vehicle (t50 5.7±0.7 vs. 6.0±0.8 min, ZM 241385 vs. vehicle, p=0.78, unpaired t-test, n=6). C: Treatment with the P2R antagonist suramin (50 µM) does not change the time-course of fEPSP recovery (t50 8.2±0.7 vs. 8.4±0.7 min, suramin vs. vehicle, p=0.87, unpaired t-test, n=6).