Fig. 1.
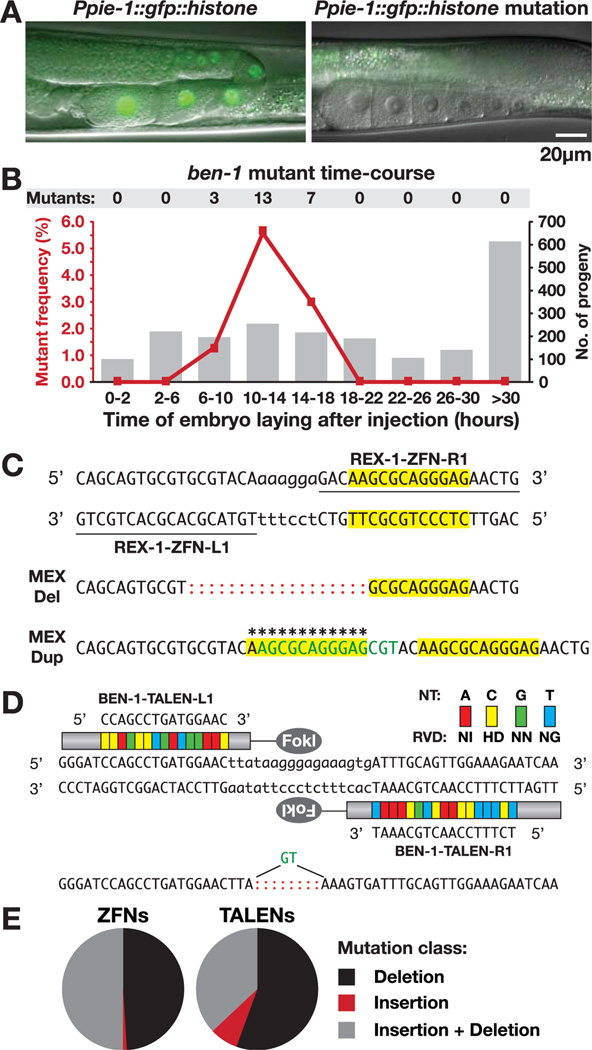
Heritable, targeted nematode mutations induced by ZFNs and TALENs. (A) Hermaphrodite gonads with an intact (left) or ZFN-disrupted (right) GFP::histone transgene. Residual signal (right) is gut autofluorescence. (B) Frequency of ben-1 mutants (left y axis, red line) from time periods after ZFN mRNA injection (x axis) relative to total progeny per period (right y axis, histogram). (C) ZFN-induced mutations in cis regulatory element rex-1 cause partial deletion and full duplication (asterisks) of MEX motif (yellow). Represented are ZFN recognition sequences (underlined), FokI cleavage region (lowercase nucleotides), insertions (green), and deletions (red colons). (D) TALEN recognition sequences in ben-1 and TALEN-induced mutation. Each RVD (colored blocks) recognizes a nucleotide (NT) in the target site. (E) Proportion of each mutation class induced by ZFNs (n=102) and TALENs (n = 27).