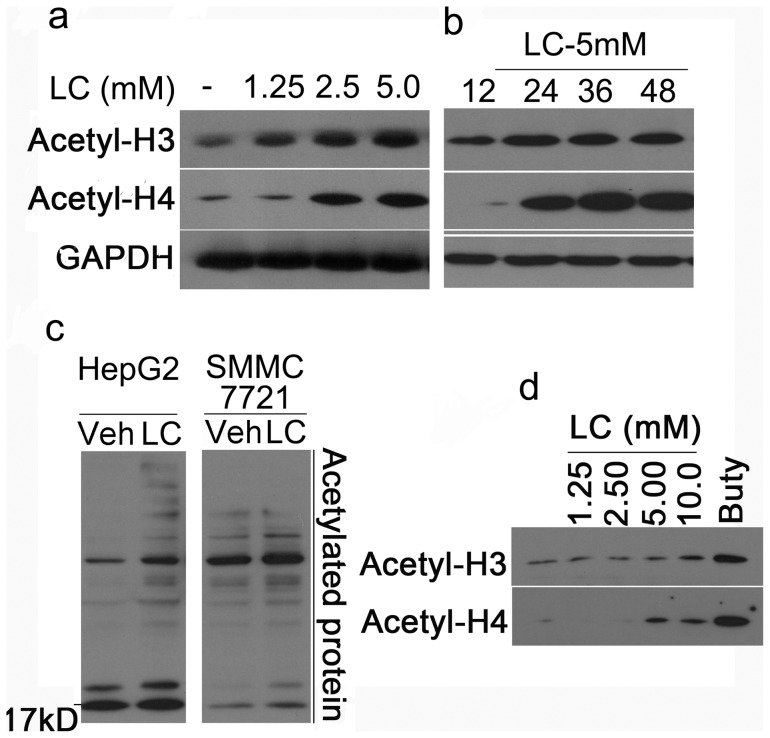
Figure 4. LC induces Histone acetylation in cultured cells.
(a) LC dose-dependently induces accumulation of acetylated histones. HepG2 cells were exposed to LC (1.25, 2.5, 5.0 mM) for 48 h, acetylated histones H3 and H4 were detected by Western blot. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (b) LC time-dependently induces accumulation of acetylated histones. HepG2 cells were treated with LC (5 mM) for different time points (12 h, 24 h, 36 h, 48 h) and acetylated histones were detected. (c) LC treatment increases lysine-acetylated protein accumulation in human HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cancer cells. Human HepG2 and SMMC-7721 cells were treated with LC (10 mM) for 12 h, and then cells were collected for Western blot to detect acetylated proteins with lysine acetylated antibody. (d) LC dose-depentently increases accumulation of acetylated histones in mouse thymocytes. Mouse thymocytes were treated with LC for 24 h, histone acetylation was detected by Western Blot. Buty (1 mM) was used as a positive control.