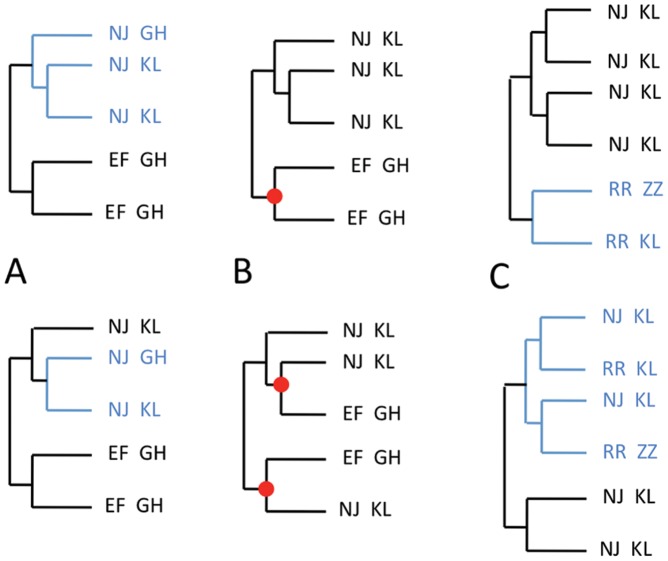
Figure 8. Pairs of blocks within trees.
Distance trees describe distinct pairs of blocks  , thought to belong to two fixed positions in an alignment. Minimal subtrees where correlation between blocks is not perfect, that is
, thought to belong to two fixed positions in an alignment. Minimal subtrees where correlation between blocks is not perfect, that is  , are highlighted in blue. In ABC, trees have the same topology and are characterized by a different labelling of the leaves with the same pairs of words. We call
, are highlighted in blue. In ABC, trees have the same topology and are characterized by a different labelling of the leaves with the same pairs of words. We call  the trees on the top and
the trees on the top and 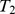 the trees on the bottom. A: the correlation score of
the trees on the bottom. A: the correlation score of 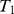 is greater than the correlation score of
is greater than the correlation score of 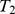 and this because for
and this because for 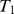 perfect correlation is disrupted on a larger subtree. B: both trees display scores of comparison and correlation
perfect correlation is disrupted on a larger subtree. B: both trees display scores of comparison and correlation 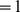 . Notice that the method does not distinguish the existence of a single mutational event transforming NJ in EF and KL in GH (top) versus a double mutational event realizing the same transformation (bottom). C: the size of subtrees displaying no perfect correlation has an impact in the correlation score of the full tree.
. Notice that the method does not distinguish the existence of a single mutational event transforming NJ in EF and KL in GH (top) versus a double mutational event realizing the same transformation (bottom). C: the size of subtrees displaying no perfect correlation has an impact in the correlation score of the full tree. 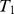 displays a greater correlation score than
displays a greater correlation score than 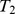 , while scores of comparison are the same.
, while scores of comparison are the same.