Figure 7.
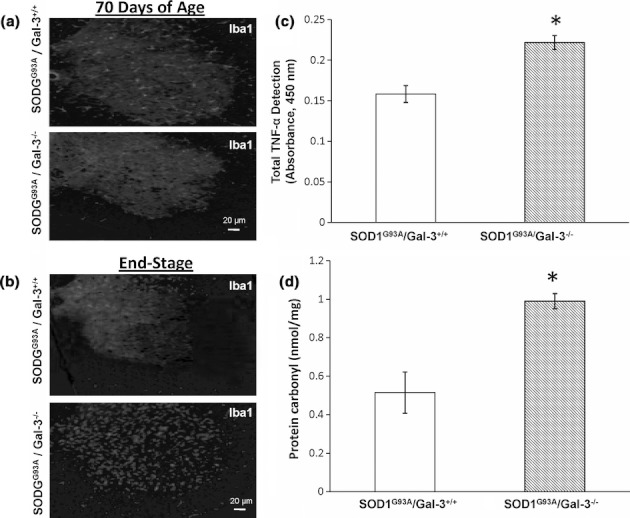
IBA1 positive cells (microglia), TNF-α, and oxidative injury are increased in C57BL6 SOD1G93A/Gal-3−/− mice compared with C57BL6 SOD1G93A/Gal-3+/+ controls at the end stage of motor neuron disease. Sections from either (a) 70-day-old or (b) end-stage (loss of righting reflex) lumbar spinal cords (n = 6 for each genotype, at each time point) were stained with anti-IBA1. Representative images are shown. (c) TNF-α and oxidative injury (d) are increased in C57BL6 SOD1G93A/Gal-3−/− mice compared with C57BL6 SOD1G93A/Gal-3+/+ controls (n = 4 for each genotype) at the end stage of motor neuron disease. TNF-α and protein carbonyls (as markers of oxidative protein modification) were assessed in homogenates from lumbar spinal cords using ELISA assays (*P < 0.05 by Student's t-test). TNF-α levels are expressed as mean ± SEM absolute absorbance values. Carbonyls were derived from a standard curve prepared from reduced oxidized BSA standards and expressed as mean ± SEM nmol/pg protein.
