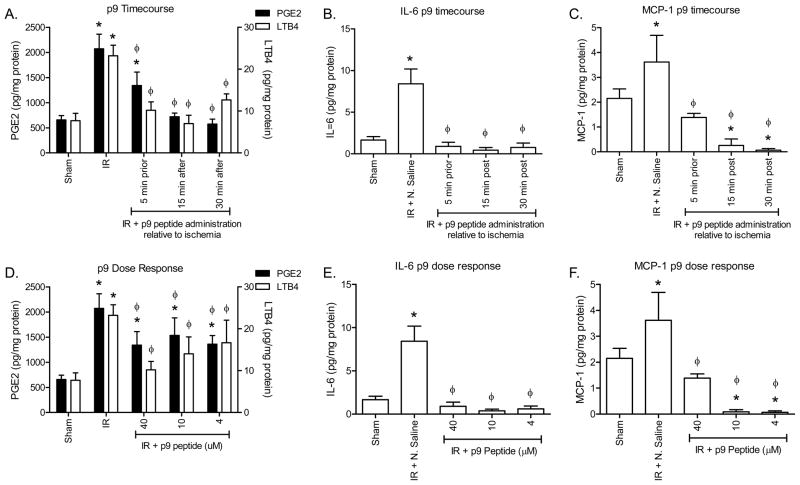
Figure 5. Peptide p9 attenuates I/R-induced intestinal eicosanoid and cytokine release in a therapeutic and dose dependent manner.
C57Bl/6 mice were subjected to Sham or I/R with or without injection of 40 μM p9 peptides, either 5 min prior to ischemia or 15 or 30 min post-ischemia (A–C). Additional mice were subjected to Sham or I/R with or without injection of 4–40 μM p9 peptide (D–F). PGE2 and LTB4 (A, D) production was measured in intestinal sections from C57Bl/6 mice with or without injection of peptides prior to Sham or I/R treatment. IL-6 (B, E) and MCP-1 (C, F) release was determined by multiplex analysis of intestinal supernatants. Values are represented as pg/mg of intestinal protein in 20 min. * = p ≤ 0.05 compared to Sham + peptide, Φ = p ≤ 0.05 compared to I/R treatment animals not receiving peptides. Each bar is representative of 4–10 animals and each treatment was performed on at least 2 separate days.