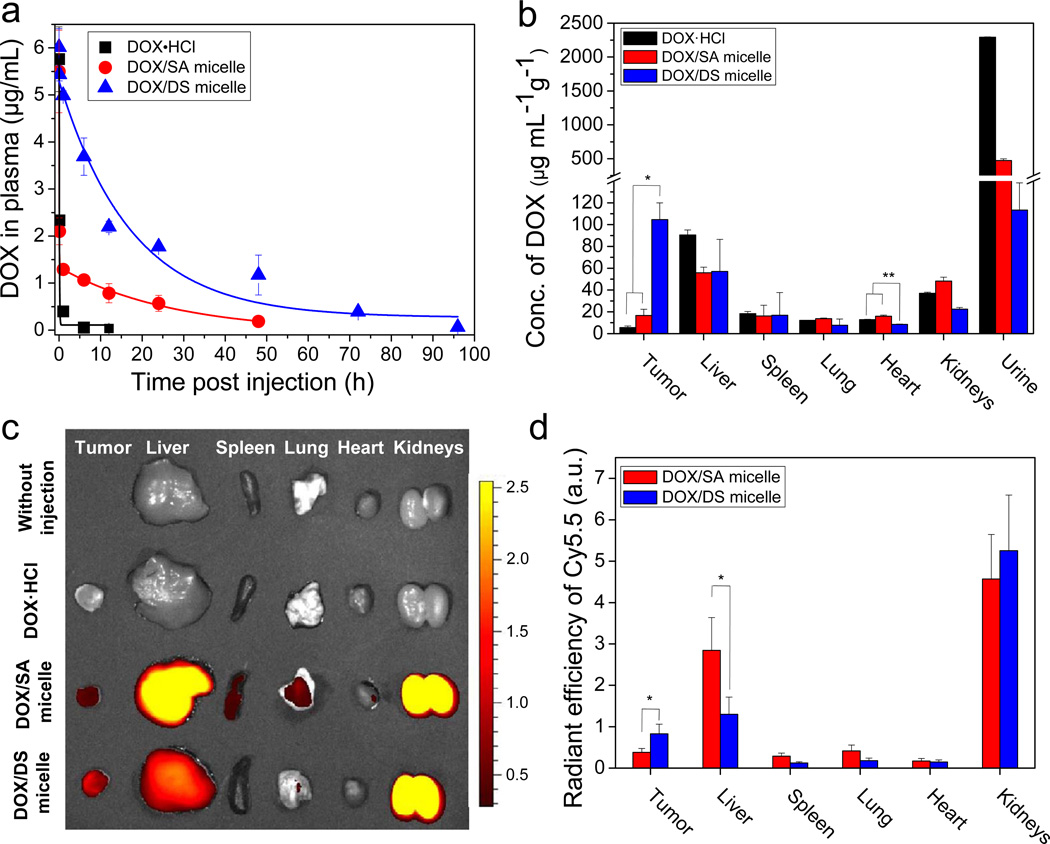
Fig. 4.
Prolonged blood retention time and improved tumor-targeting efficacy of DOX via DS micelles. (a) Blood retention kinetics of DOX·HCl, DOX loaded in SA and DS micelles in mice. DOX·HCl (at 4 mg/kg), DOX/SA and DOX/DS micelles (at 4 mg DOX equiv/kg) were intravenously injected. The data were fitted with a one-compartment model (y = Ae(-x/t) + y0) for DOX·HCl and DOX/DS micelle groups or a two-compartment model (y = A1e(-x/t1) + A2e(-x/t2) + y0) for DOX/SA micelle group. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (n=5). (b) Tissue distribution of DOX at 1 day-post injection. DOX·HCl (at 4 mg/kg), DOX/SA(-Cy5.5) and DOX/DS(-Cy5.5) micelles (at 4 mg DOX equiv/kg, with similar absorption intensity of Cy5.5) were intravenously injected to M109 bearing mice. means ± SEM (n=4). *P < 0.005; **P < 0.001. (c) Fluorescent image of tissue distribution of Cy5.5-labeled SA and DS micelles at 1 day-post injection. (d) Quantitative analysis of Cy5.5-labeled SA and DS micelles in tissues. Values are means ± SEM (n=4). *P < 0.05