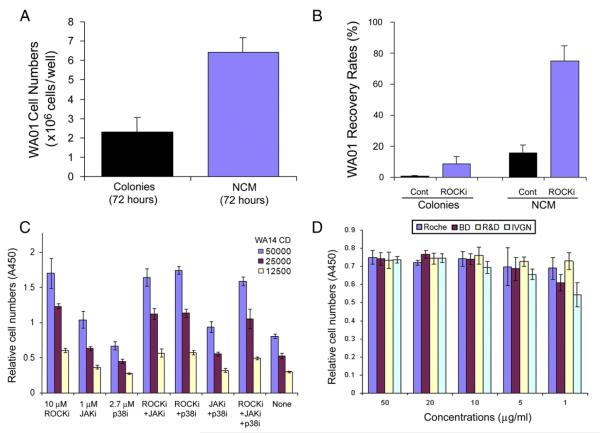
Figure 6.
Applications of NCM culture. (A) Comparison of cell yields under NCM to conventional colony-type culture of hESCs (e.g., WA01 cells) on MEF feeder layers. (B) Recovery rate of WA01 cells: WA01 cells were cultured under ncm conditions, frozen in liquid nitrogen, and thawed in the presence or absence of 10 μM ROCKi. WA01 colonies, grown on MEFs, were used for comparison. The cell numbers were counted 24 h after thawing. (C) High throughput assay of growth conditions for hESCs in a 96-well format: to demonstrate the ease with which the NCM method may be used in high throughput applications, we performed single-cell plating efficiency assays of WA14 hESCs under NCM conditions with various small-molecules and their combinations. (D) Cell survival assays: to test different sources (i.e., purchased from Roche, R&D Systems, Invitrogen, and BD Biosciences; abbreviated as Roche, R&D, IVGN, and BD respectively) and concentrations of fibronectin on plating efficiency using a 96-well format: approximately 31,000 WA14 cells were plated in 10% KSR-X/TeSR2 on BD Purecoat (BD Biosciences), additionally coated with a range of concentrations of human fibronectin from different vendors. After 24 h, the cells were subjected to the CCK-8 survival assay (Dojino Molecular Technologies, Rockville, MD) by measuring the absorbance at 450 nm (A450). Abbreviations: Cont, drug untreated control; JAKi, JAK inhibitor I; p38i, the p38MAPK inhibitor SB203580; ROCKi, the ROCK inhibitor Y27632; WA14 CD, WA14 cell density.